A spherical niobium droplet of diameter D = 3 mm is levitated by an acoustical technique in
Question:
A spherical niobium droplet of diameter D = 3 mm is levitated by an acoustical technique in a vacuum chamber having walls that are diffuse and gray with an emissivity of ɛw =0.8 and a temperature of Tw = 300 K. The niobium surface is diffuse and has the prescribed spectral emissivity distribution.
Two heating methods for maintaining the drop at its melting temperature, Tmp = 2741 K, are to be investigated.
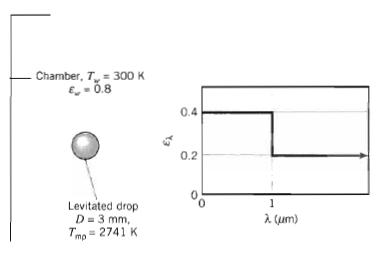 (a) The effect of applying a radio frequency (RF) field to the drop is to create a uniform internal generation rate, q̇ (W/m), within the drop. Calculate the value of q̇ required to maintain the drop at its melting temperature.
(a) The effect of applying a radio frequency (RF) field to the drop is to create a uniform internal generation rate, q̇ (W/m), within the drop. Calculate the value of q̇ required to maintain the drop at its melting temperature.
(b) A laser beam, having a diameter larger than that of the drop and operating at 10.6 μm, irradiates the drop. Determine the irradiation, Glaser (W/mm2), required to maintain the drop at its melting temperature. What irradiation would be required if the laser operating wavelength were 0.632 μm?
(c) Estimate the time it would take for the drop to cool to 400 K if the RF field or laser heating were terminated.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





