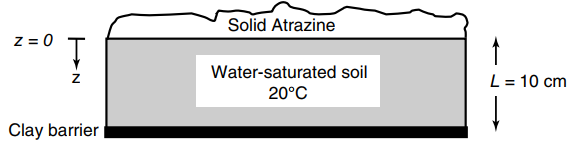
The pesticide Atrazine (C 8 H 14 C1N 5 , mol wt. 216 g/ mol) degrades in
Question:
a. What is the molecular diffusion coefficient of Atrazine in water (DAB) at 20°C, and the effective diffusion coefficient (DAe) in the water-saturated soil? The specific molar volume of Atrazine is 170 cm3/gmole, at its normal boiling point. The effective diffusion coefficient is estimated by DAe = ε2 DAB (A = Atrazine, B = water), with a void fraction (ε) of 0.6. The effective diffusion coefficient accounts for the fact that not all of the soil is liquid water.
b. What is the concentration of Atrazine (mmole/L) in the water-saturated soil at the clay barrier (z = L)? It may be assumed that the process is at steady state with a one dimensional flux of A in the z-direction.
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





