The area under the ROC curve is 65%. What does it mean? Orthopedics Piriformis syndrome is a
Question:
Orthopedics
Piriformis syndrome is a pelvic condition that involves malfunction of the piriformis muscle (a deep buttock muscle), which often causes back and buttock pain with sciatica (pain radiating down the leg). An electrophysiologic test to detect piriformis syndrome involves measuring nerveconduction
velocity (NCV) at two nerves in the leg (the tibial and peroneal nerves) with the leg flexed in a specific position. Increases in NCV in these nerves are often associated with piriformis syndrome. The resulting test, called the flexion abduction and internal rotation (FAIR) test, is positive if the average NCV in these nerves is delayed by 2+ seconds relative to normal.
A small study compared the FAIR test results with patient self-reports of how they feel on a visual analog scale (VAS) of 0€“10, with 0 indicating no pain and 10 very severe pain. The results were as shown in Table 3.17.
Table 3.17: FAIR test results on piriformis syndrome patients
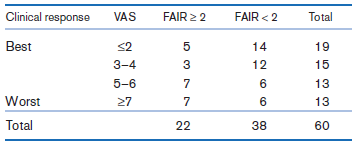
Suppose physicians consider the FAIR test the gold standard, with a FAIR test result of ‰¥ 2 defined as a true positive and a FAIR test result of < 2 defined as a true negative. Suppose a VAS of ‰¤ 4 is considered a good clinical response based on self-report (a test-negative) and a VAS of ‰¥ 5 is considered a bad clinical response (a test-positive).
Step by Step Answer:






