Part I of this case, presented in Chapter 3, discussed the situation of DLeon Inc., a regional
Question:
Part I of this case, presented in Chapter 3, discussed the situation of D’Leon Inc., a regional snack foods producer, after an expansion program. D’Leon had increased plant capacity and undertaken a major marketing campaign in an attempt to “go national.” Thus far, sales have not been up to the forecasted level, costs have been higher than were projected, and a large loss occurred in 2021 rather than the expected profit. As a result, its managers, directors, and investors are concerned about the firm’s survival.
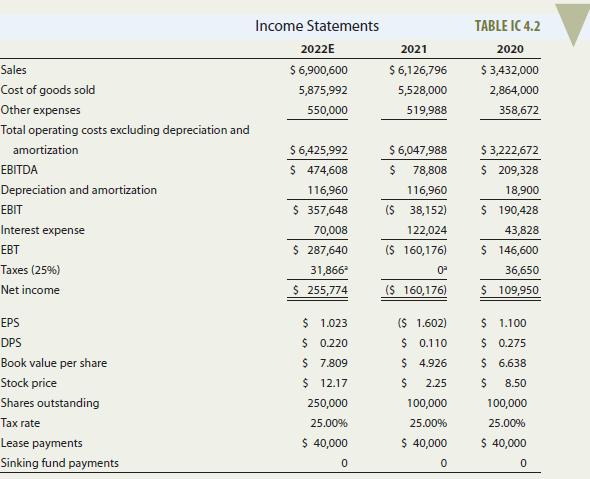
Donna Jamison was brought in as assistant to Fred Campo, D’Leon’s chairman, who had the task of getting the company back into a sound financial position. D’Leon’s 2020 and 2021 balance sheets and income statements, together with projections for 2022, are given in Tables IC 4.1 and IC 4.2. Note that D‘Leon is exempt from the interest deduction limitation because its average gross receipts for the prior 3 years was less than $25 million. So 100% of its interest expense is deductible. Also, many of D‘Leon‘s assets have lives greater than 20 years and thus qualify for the alternative depreciation system (straight line) rather than the 100%
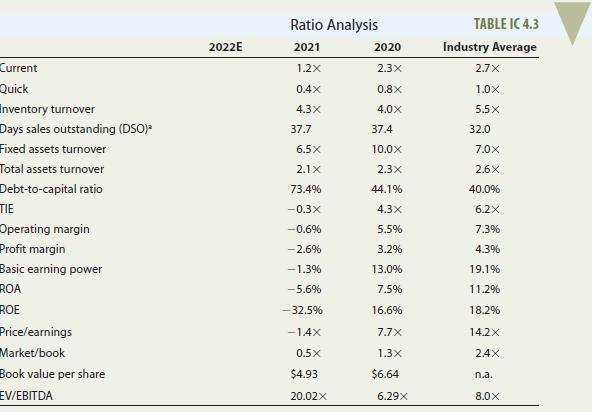
bonus depreciation. In addition, Table IC 4.3 gives the company’s 2020 and 2021 financial ratios, together with industry average data. The 2022 projected financial statement data represent Jamison’s and Campo’s best guess for 2022 results, assuming that some new financing is arranged to get the company “over the hump.”
Jamison examined monthly data for 2021 (not given in the case), and she detected an improving pattern during the year. Monthly sales were rising, costs were falling, and large losses in the early months had turned to a small profit by December. Thus, the annual data look somewhat worse than final monthly data.
Also, it appears to be taking longer for the advertising program to get the message out, for the new sales offices to generate sales, and for the new manufacturing facilities to operate efficiently. In other words, the lags between spending money and deriving benefits were longer than D’Leon’s managers had anticipated.
For these reasons, Jamison and Campo see hope for the company—provided it can survive in the short run.
Jamison must prepare an analysis of where the company is now, what it must do to regain its financial health, and what actions should be taken. Your assignment is to help her answer the following questions.
Provide clear explanations, not yes or no answers.
a. Why are ratios useful? What are the five major categories of ratios?
b. Calculate D’Leon’s 2022 current and quick ratios based on the projected balance sheet and income statement data. What can you say about the company’s liquidity positions in 2020, in 2021, and as projected for 2022? We often think of ratios as being useful (1) to managers to help run the business,
(2) to bankers for credit analysis, and (3) to stockholders for stock valuation. Would these different types of analysts have an equal interest in the company’s liquidity ratios? Explain your answer.
c. Calculate the 2022 inventory turnover, days sales outstanding (DSO), fixed assets turnover, and total assets turnover. How does D’Leon’s utilization of assets stack up against other firms in the industry?
d. Calculate the 2022 debt-to-capital and times-interest-earned ratios. How does D’Leon compare with the industry with respect to financial leverage? What can you conclude from these ratios?
e. Calculate the 2022 operating margin, profit margin, basic earning power (BEP), return on assets (ROA), and return on equity (ROE). What can you say about these ratios?
f. Calculate the 2022 price/earnings ratio and market/book ratio. Do these ratios indicate that investors are expected to have a high or low opinion of the company?
g. Use the DuPont equation to provide a summary and overview of D’Leon’s financial condition as projected for 2022. What are the firm’s major strengths and weaknesses?
h. Use the following simplified 2022 balance sheet to show, in general terms, how an improvement in the DSO would tend to affect the stock price. For example, if the company could improve its collection procedures and thereby lower its DSO from 46.4 days to the 32-day industry average without affecting sales, how would that change “ripple through” the financial statements (shown in thousands in the following table) and influence the stock price?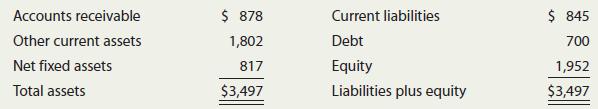
i. Does it appear that inventories could be adjusted? If so, how should that adjustment affect D’Leon’s profitability and stock price?
j. In 2021, the company paid its suppliers much later than the due dates; also, it was not maintaining financial ratios at levels called for in its bank loan agreements. Therefore, suppliers could cut the company off, and its bank could refuse to renew the loan when it comes due in 90 days. On the basis of data provided, would you, as a credit manager, continue to sell to D’Leon on credit? (You could demand cash on delivery—
that is, sell on terms of COD—but that might cause D’Leon to stop buying from your company.) Similarly, if you were the bank loan officer, would you recommend renewing the loan or demanding its repayment?
Would your actions be influenced if, in early 2022, D’Leon showed you its 2022 projections along with proof that it was going to raise more than $1.2 million of new equity?
k. In hindsight, what should D’Leon have done in 2020?
l. What are some potential problems and limitations of financial ratio analysis?
m. What are some qualitative factors that analysts should consider when evaluating a company’s likely future financial performance?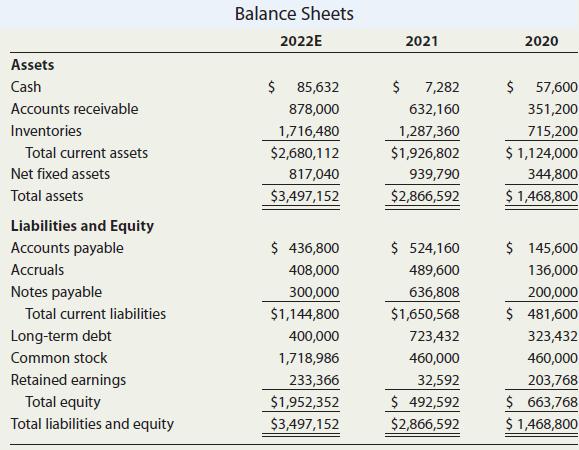
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Financial Management
ISBN: 9780357517574
16th Edition
Authors: Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston





