A thermodynamic analysis of a proposed Brayton cycle gas turbine yields P = 5 MW of net
Question:
A thermodynamic analysis of a proposed Brayton cycle gas turbine yields P = 5 MW of net power production. The compressor, at an average temperature of Tc = 400°C, is driven by the turbine at an average temperature of Th = 1000°C by way of an L = 1-m-long, d = 70-mmdiameter shaft of thermal conductivity k 40 W/m · K.
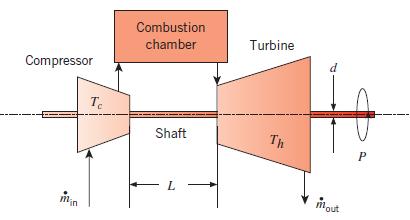
(a) Compare the steady-state conduction rate through the shaft connecting the hot turbine to the warm compressor to the net power predicted by the thermodynamics- based analysis.
(b) A research team proposes to scale down the gas turbine of part (a), keeping all dimensions in the same proportions. The team assumes that the same hot and cold temperatures exist as in part (a) and that the net power output of the gas turbine is proportional to the overall volume of the device. Plot the ratio of the conduction through the shaft to the net power output of the turbine over the range 0.005 m ≤ L ≤ 1 m. Is a scaled-down device with L = 0.005 m feasible?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9780470501979
7th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine, Frank P. Incropera, David P. DeWitt





