(A) Glycolysis involves ten biochemical reactions. The first two reactions of the glycolysis cycle are Calculate the...
Question:
(A) Glycolysis involves ten biochemical reactions. The first two reactions of the glycolysis cycle are
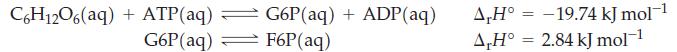
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of F6P(aq) generated in the glycolysis cycle at normal body temperature, 37 °C, starting with [C6H12O6(aq)] = 1.20 x 10-6 M; [ATP(aq)] = 10-4 M; and [ADP(aq)] = 10-2 M. The equilibrium constant for the first reaction is 4.630 x 103; for the second reaction it is 2.76 x 10-1. During a fever body temperature increases. Will [G6P] increase or decrease with an increase with temperature?
(B) A procedure calls for adding 0.100 mol of Br2(g) at 25 °C to a reaction. The only source of bromine in the laboratory is a bottle of liquid bromine.
(a) Given the following data, what size container (in liters) must be used to extract enough Br2(g) for this reaction? The equilibrium constant at 298 K for the reaction Br2(g) ⇌ 2 Br(g) is K = 3.30 x 10-29. The vapor pressure of liquid bromine is 0.289 atm.
(b) At 1000 K the equilibrium constant for the reaction Br2(g) ⇌ 2 Br(g) is 3.4 x 10-5. What size vessel (in liters) will be needed if the temperature of the vapor is raised to 1000 K?
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





