Electricity can be produced by the action of microbes on organic matter in soil or waste water.
Question:
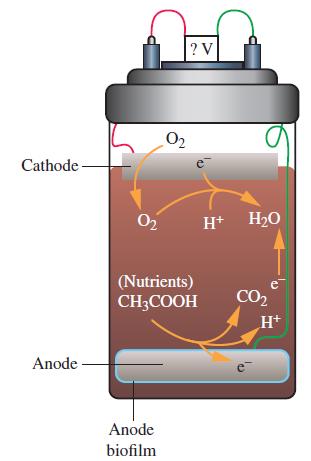
Electricity can be produced by the action of microbes on organic matter in soil or waste water. For example, in the fuel cell shown on the right, the anode produces electrons by the oxidation of organic compounds in soil. The anode is coated with a film containing geobacter metallireducens, a bacterium that can oxidize organic compounds, such as acetic acid, to carbon dioxide. The electrons produced at the anode are then used at the cathode to reduce dissolved oxygen to water. The redox couple CO2/CH3COO- has a biological standard reduction potential (see Exercise 109) of – 0.29 V. The redox couple O2/H2O has a biological standard reduction potential of 0.82 V.
(a) Write the anode half-cell reaction.
(b) Write the cathode half-cell reaction.
(c) Calculate the overall standard cell potential.
(d) What role does the microbe play in this electrochemical process?
Exercise 109
Some electrochemical cells employ large biological molecules known as enzymes. An enzyme increases the rate of a biochemical reaction. Some enzymes perform oxidation reactions, and some others perform reduction reactions. An electrochemical cell based on the use of enzymes is given in the following illustration.
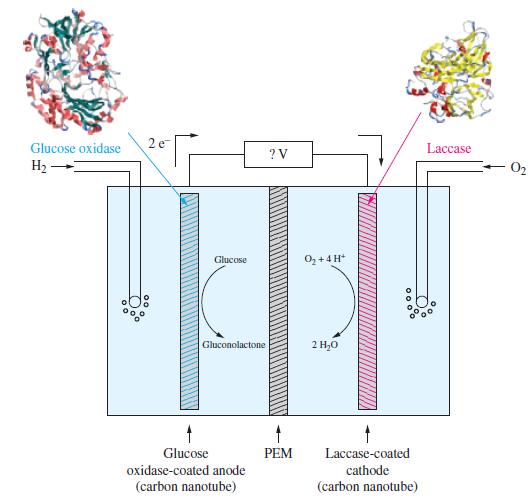
The half-cell reactions for electrochemical cell and the corresponding reduction potentials are given below. The symbol E°’ is used here because these values refer to the biological standard state: 37 °C, aH+ = 10-7, all other activities equal to 1.
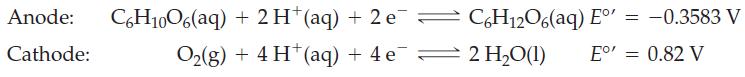
Write an equation for the overall reaction occurring in this electrochemical cell.
Write a cell diagram for this battery.
Calculate the standard cell potential for the electrochemical reaction.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





