Some substances that are only very slightly soluble in water will spread over the surface of water
Question:
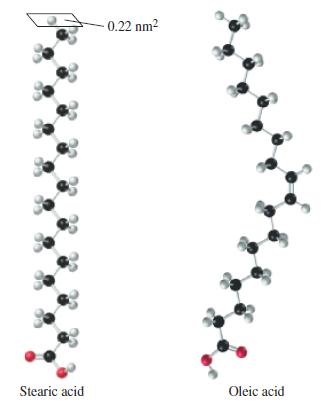
Some substances that are only very slightly soluble in water will spread over the surface of water to produce a film that is called a monolayer because it is only one molecule thick. A practical use of this phenomenon is to cover ponds to reduce the loss of water by evaporation. Stearic acid forms a monolayer on water. The molecules are arranged upright and in contact with one another, rather like pencils tightly packed and standing upright in a coffee mug. The model below represents an individual stearic acid molecule in the monolayer.
(a) How many square meters of water surface would be covered by a monolayer made from 10.0 g of stearic acid?
(b) If stearic acid has a density of 0.85 g/cm3, estimate the length (in nanometers) of a stearic acid molecule.
(c) A very dilute solution of oleic acid in liquid pentane is prepared in the following way:
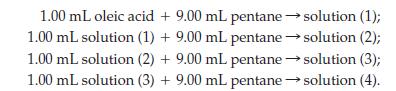
A 0.10 mL sample of solution (4) is spread in a monolayer on water. The area covered by the monolayer is 85 cm2. Assume that oleic acid molecules are arranged in the same way as described for stearic acid, and that the cross-sectional area of the molecule is 4.6 x 10-15 cm2. The density of oleic acid is 0.895 g/mL. Use these data to obtain an approximate value of Avogadro’s number.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





