An aluminum heat (operatorname{sink}(k=230 mathrm{~W} / mathrm{m} cdot mathrm{K})), used to cool an array of electronic chips,
Question:
An aluminum heat \(\operatorname{sink}(k=230 \mathrm{~W} / \mathrm{m} \cdot \mathrm{K})\), used to cool an array of electronic chips, consists of a square channel of inner width \(w=30 \mathrm{~mm}\), through which liquid flow may be assumed to maintain a uniform surface temperature of \(T_{1}=20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The outer width and length of the channel are \(W=40 \mathrm{~mm}\) and \(L=160 \mathrm{~mm}\), respectively.
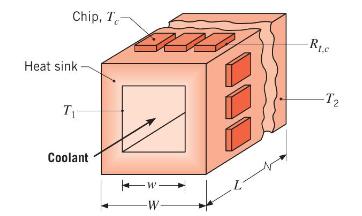
If \(N=120\) chips attached to the outer surfaces of the heat sink maintain an approximately uniform surface temperature of \(T_{2}=60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and all of the heat dissipated by the chips is assumed to be transferred to the coolant, what is the heat dissipation per chip? If the contact resistance between each chip and the heat sink is \(R_{t, c}=0.1 \mathrm{~K} / \mathrm{W}\), what is the chip temperature?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781119220442
8th Edition
Authors: Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine





