Consider a long solid bar whose thermal conductivity is k = 5 W/m K and whose
Question:
Consider a long solid bar whose thermal conductivity is k = 5 W/m · K and whose cross section is given in the figure. The top surface of the bar is maintained at 50°C while the bottom surface is maintained at 120°C. The left surface is insulated and the remaining three surfaces are subjected to convection with ambient air at T∞ 5 25°C with a heat transfer coefficient of h = 40 W/m2 · K. Using the finite difference method with a mesh size of Δx = Δy = 10 cm,
(a) Obtain the finite difference formulation of this problem for steady two-dimensional heat transfer
(b) Determine the unknown nodal temperatures by solving those equations.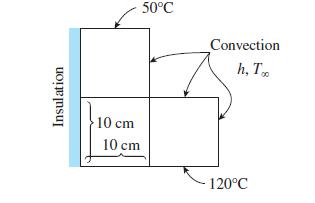
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Heat And Mass Transfer Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073398181
5th Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, Afshin Ghajar
Question Posted:





