Question: Project Management Methodology (Methodology)Group Assignment and Presentation. Professor to divide the class in groups and assign Methodologies from Exhibit 7.1. Groups will go outside of
Project Management Methodology (“Methodology”)—Group Assignment and Presentation. Professor to divide the class in groups and assign Methodologies from Exhibit 7.1. Groups will go outside of the textbook (i.e., IT literature and/or any other valid external source) to summarize and present to the class the Methodology/ies assigned. The presentation should:
Exhibit 7.1
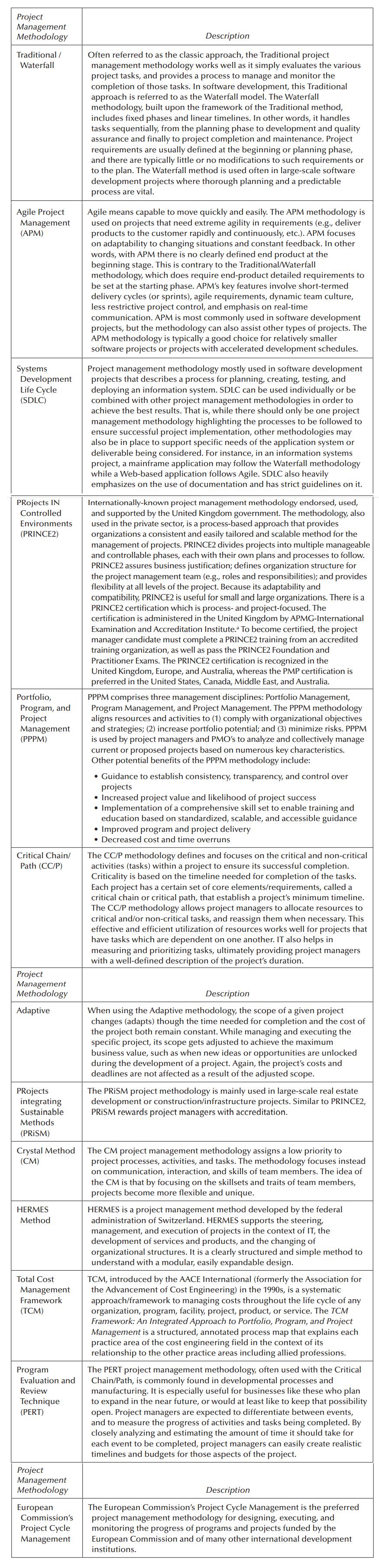
a. Provide an overall explanation of the Methodology, including, but not limited to: definition; purpose and objectives; whether it is United States or International-based; industries where Methodology/ies has/have been used; etc.
b. Highlight the benefits and challenges of the Methodology to project managers.
c. Include examples of organizations that have used the particular Methodology and, if available, describe their overall experience.
d. Be submitted in power-point-presentation format with a cover page and a reference section at the end. The submitted file should be between 8 and 10 pages long, including cover page and references.
Project Management Methodology Traditional / Waterfall Agile Project Management (APM) Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) PRojects IN Controlled Environments (PRINCE2) Portfolio, Program, and Project Management (PPPM) Critical Chain/ Path (CC/P) Project Management Methodology Adaptive PRojects integrating Sustainable Methods (PRISM) Crystal Method (CM) HERMES Method Total Cost Management Framework (TCM) Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) Project Management Methodology European Commission's Project Cycle Management Description Often referred to as the classic approach, the Traditional project management methodology works well as it simply evaluates the various project tasks, and provides a process to manage and monitor the completion of those tasks. In software development, this Traditional approach is referred to as the Waterfall model. The Waterfall methodology, built upon the framework of the Traditional method, includes fixed phases and linear timelines. In other words, it handles tasks sequentially, from the planning phase to development and quality assurance and finally to project completion and maintenance. Project requirements are usually defined at the beginning or planning phase, and there are typically little or no modifications to such requirements or to the plan. The Waterfall method is used often in large-scale software development projects where thorough planning and a predictable process are vital. Agile means capable to move quickly and easily. The APM methodology is used on projects that need extreme agility in requirements (e.g., deliver products to the customer rapidly and continuously, etc.). APM focuses on adaptability to changing situations and constant feedback. In other words, with APM there is no clearly defined end product at the beginning stage. This is contrary to the Traditional/Waterfall methodology, which does require end-product detailed requirements to be set at the starting phase. APM's key features involve short-termed delivery cycles (or sprints), agile requirements, dynamic team culture, less restrictive project control, and emphasis on real-time communication. APM is most commonly used in software development projects, but the methodology can also assist other types of projects. The APM methodology is typically a good choice for relatively smaller software projects or projects with accelerated development schedules. Project management methodology mostly used in software development projects that describes a process for planning, creating, testing, and deploying an information system. SDLC can be used individually or be combined with other project management methodologies in order to achieve the best results. That is, while there should only be one project management methodology highlighting the processes to be followed to ensure successful project implementation, other methodologies may also be in place to support specific needs of the application system or deliverable being considered. For instance, in an information systems project, a mainframe application may follow the Waterfall methodology while a Web-based application follows Agile. SDLC also heavily emphasizes on the use of documentation and has strict guidelines on it. Internationally-known project management methodology endorsed, used, and supported by the United Kingdom government. The methodology, also used in the private sector, is a process-based approach that provides organizations a consistent and easily tailored and scalable method for the management of projects. PRINCE2 divides projects into multiple manageable and controllable phases, each with their own plans and processes to follow. PRINCE2 assures business justification; defines organization structure for the project management team (e.g., roles and responsibilities); and provides flexibility at all levels of the project. Because its adaptability and compatibility, PRINCE2 is useful for small and large organizations. There is a PRINCE2 certification which is process- and project-focused. The certification is administered in the United Kingdom by APMG-International Examination and Accreditation Institute. To become certified, the project manager candidate must complete a PRINCE2 training from an accredited training organization, as well as pass the PRINCE2 Foundation and Practitioner Exams. The PRINCE2 certification is recognized in the United Kingdom, Europe, and Australia, whereas the PMP certification is preferred in the United States, Canada, Middle East, and Australia. PPPM comprises three management disciplines: Portfolio Management, Program Management, and Project Management. The PPPM methodology aligns resources and activities to (1) comply with organizational objectives and strategies; (2) increase portfolio potential; and (3) minimize risks. PPPM is used by project managers and PMO's to analyze and collectively manage current or proposed projects based on numerous key characteristics. Other potential benefits of the PPPM methodology include: Guidance to establish consistency, transparency, and control over projects Increased project value and likelihood of project success Implementation of a comprehensive skill set to enable training and education based on standardized, scalable, and accessible guidance Improved program and project delivery Decreased cost and time overruns The CC/P methodology defines and focuses on the critical and non-critical activities (tasks) within a project to ensure its successful completion. Criticality is based on the timeline needed for completion of the tasks. Each project has a certain set of core elements/requirements, called a critical chain or critical path, that establish a project's minimum timeline. The CC/P methodology allows project managers to allocate resources to critical and/or non-critical tasks, and reassign them when necessary. This effective and efficient utilization of resources works well for projects that have tasks which are dependent on one another. IT also helps in measuring and prioritizing tasks, ultimately providing project managers with a well-defined description of the project's duration. Description When using the Adaptive methodology, the scope of a given project changes (adapts) though the time needed for completion and the cost of the project both remain constant. While managing and executing the specific project, its scope gets adjusted to achieve the maximum business value, such as when new ideas or opportunities are unlocked during the development of a project. Again, the project's costs and deadlines are not affected as a result of the adjusted scope. The PRISM project methodology is mainly used in large-scale real estate development or construction/infrastructure projects. Similar to PRINCE2, PRISM rewards project managers with accreditation. The CM project management methodology assigns a low priority to project processes, activities, and tasks. The methodology focuses instead on communication, interaction, and skills of team members. The idea of the CM is that by focusing on the skillsets and traits of team members, projects become more flexible and unique. HERMES is a project management method developed by the federal administration of Switzerland. HERMES supports the steering, management, and execution of projects in the context of IT, the development of services and products, and the changing of organizational structures. It is a clearly structured and simple method to understand with a modular, easily expandable design. TCM, introduced by the AACE International (formerly the Association for the Advancement of Cost Engineering) in the 1990s, is a systematic approach/framework to managing costs throughout the life cycle of any organization, program, facility, project, product, or service. The TCM Framework: An Integrated Approach to Portfolio, Program, and Project Management is a structured, annotated process map that explains each practice area of the cost engineering field in the context of its relationship to the other practice areas including allied professions. The PERT project management methodology, often used with the Critical Chain/Path, is commonly found in developmental processes and manufacturing. It is especially useful for businesses like these who plan to expand in the near future, or would at least like to keep that possibility open. Project managers are expected to differentiate between events, and to measure the progress of activities and tasks being completed. By closely analyzing and estimating the amount of time it should take for each event to be completed, project managers can easily create realistic timelines and budgets for those aspects of the project. Description The European Commission's Project Cycle Management is the preferred project management methodology for designing, executing, and monitoring the progress of programs and projects funded by the European Commission and of many other international development institutions.
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
It seems you are tasked with a group assignment and presentation on a specific project management methodology As I cannot choose the methodology for y... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


