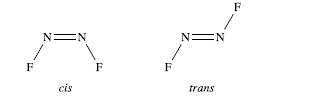
(a) The structures of cis- and trans-N 2 F 2 were shown in worked example 3.1. Give...
Question:
(a) The structures of cis- and trans-N2F2 were shown in worked example 3.1. Give an appropriate hybridization scheme for the N atoms in each isomer.
(b) What hybridization scheme is appropriate for the O atoms in H2O2 (Fig. 2.1)?
Figure 2.1
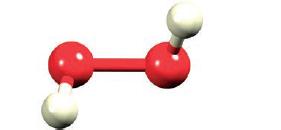
Data from Example 3.1
How do the rotation axes and planes of symmetry in cis- and trans-N2F2 differ?
First draw the structures of cis- and trans-N2F2; both are planar molecules.
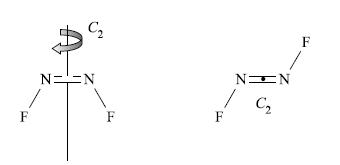
1. The identity operator E applies to each isomer.
2. Each isomer possesses a plane of symmetry which contains the molecular framework. However, their labels differ (see point 5 below).
3. The cis-isomer contains a C2 axis which lies in the plane of the molecule, but the trans-isomer contains a C2 axis which bisects the N—N bond and is perpendicular to the plane of the molecule.
4. The cis- (but not the trans-) isomer contains a mirror plane, σv, lying perpendicular to the plane of the molecule and bisecting the N—N bond:
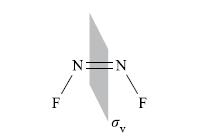
5. The consequence of the different types of C2 axes, and the presence of the σv plane in the cis-isomer, is that the symmetry planes containing the cis- and trans-N2F2 molecular frameworks are labelled σv' and σh respectively.
Step by Step Answer:






