Buy Low Sell High Corp. issues bonds to finance the acquisition of marketable securities. On January 1,
Question:
Buy Low Sell High Corp. issues bonds to finance the acquisition of marketable securities. On January 1, 2019, Buy Low sells $1,000,000 in three-year, 5% bonds for $970,000. Interest is payable on June 30 and December 31 each year. The corporate year-end is December 31.
Buy Low’s junior accountant, Bob Blades, has been asked to prepare a bond discount amortization spreadsheet. Bob is not sure whether he should use the straight-line or effective interest method to amortize the discount, so he prepares both.
Required:
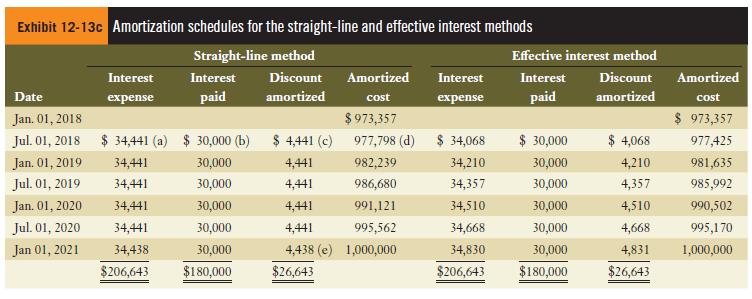
a. Complete a bond amortization spreadsheet that contrasts the use of the straight-line method and the effective interest method. Use the format that follows as employed in Exhibit 12-13c.

Prepare journal entries to record:
b. The issuance of the bonds on January 1, 2019.
c. Payment of interest and related amortization on June 30, 2019, under the straight-line method.
d. Payment of interest and related amortization on June 30, 2019, under the effective interest method.
e. Retirement of the bonds on December 31, 2021, assuming that the final interest payment has already been recorded in the company’s books.
f. Compare and contrast the two methods. Interest expense in the first period is higher under which method for bonds sold at a discount? For bonds sold at a premium? Why does IFRS require public companies to use the effective interest method? Why do the Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises allow companies to use the straight-line method?
Exhibit 12-13c

Step by Step Answer:






