Question: In the?parallel-machine-scheduling problem, we are given?n?jobs,?J 1 , J 2 , . . . ,J n , where each job?J k has an associated nonnegative
In the?parallel-machine-scheduling problem, we are given?n?jobs,?J1, J2, . . . ,Jn, where each job?Jk has an associated nonnegative processing time of?pk. We are also given?m?identical machines,?M1, M2, . . . ,Mm. Any job can run on any machine.
A?schedule?specifies, for each job?Jk, the machine on which it runs and the time period during which it runs. Each job?Jk must run on some machine?Mi for?pk?consecutive time units, and during that time period no other job may run on?Mi. Let?Ck denote the?completion time?of job?Jk, that is, the time at which job?Jk completes processing. Given a schedule, we define?Cmax =?max1???j???n?Cj to be the?makespan?of the schedule. The goal is to find a schedule whose makespan is minimum.
For example, suppose that we have two machines?M1 and?M2 and that we have four jobs?J1, J2, J3, J4, with?p1 =?2,?p2 =?12,?p3 =?4, and?p4 =?5. Then one possible schedule runs, on machine?M1, job?J1 followed by job?J2, and on machine?M2, it runs job?J4 followed by job?J3. For this schedule,?C1 =?2,?C2 =?14,
C3 =?9,?C4 =?5, and?Cmax =?14. An optimal schedule runs?J2 on machineM1, and it runs jobs?J1,?J3, and?J4 on machine?M2. For this schedule,?C1 =?2,?C2 =?12,?C3 =?6,?C4 =?11, and?Cmax =?12.
Given a parallel-machine-scheduling problem, we let?C*max denote the makespan of an optimal schedule.
a.?Show that the optimal makespan is at least as large as the greatest processing time, that is,
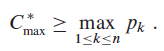
b.?Show that the optimal makespan is at least as large as the average machine load, that is,
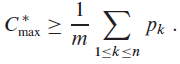
Suppose that we use the following greedy algorithm for parallel machine scheduling. whenever a machine is idle, schedule any job that has not yet been scheduled.
c.?Write pseudocode to implement this greedy algorithm. What is the running time of your algorithm?
d.?For the schedule returned by the greedy algorithm, show that
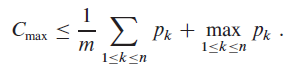
Conclude that this algorithm is a polynomial-time 2-approximation algorithm.
|C* max Pe 1
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a This can be shown using the pigeonhole principle Suppose that the greatest processing time is p an... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


