Question: Consider a liquid (constant density) pumped steadily along a pipe of constant diameter. a. We know from Chapter 5 that the mass flow rate into
Consider a liquid (constant density) pumped steadily along a pipe of constant diameter.
a. We know from Chapter 5 that the mass flow rate into any section of the pipe must equal the mass flow rate out of that section.What does Equation 7.4 tell us about the outlet average velocity compared with the inlet average velocity? Is this answer different if the fluid is flowing uphill? downhill?
Equation 7.4
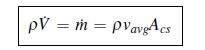 b. If the pipe is horizontal, what happens to the pressure of the liquid as it is pumped through the pipe? What factor most strongly affects that phenomenon?
b. If the pipe is horizontal, what happens to the pressure of the liquid as it is pumped through the pipe? What factor most strongly affects that phenomenon?
c. If the liquid is pumped up a hill, what is happening to the potential energy of the liquid? Therefore, will the numerical value of the work term ws in the mechanical energy equation be positive, or negative? What does that imply about what the pump does to the energy of the liquid?
pVm = pvavgAcs
Step by Step Solution
3.33 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Equation 74 says as much average cs PVmv avg The formula A cs multiplies the mass flow rate m by the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


