Gigabyte, Inc. manufactures three products for the computer industry: Gismos (product G): annual sales, 8,000 units Thingamajigs
Question:
Gigabyte, Inc. manufactures three products for the computer industry:
Gismos (product G): annual sales, 8,000 units Thingamajigs (product T): annual sales, 15,000 units Whatchamacallits (product W): annual sales, 4,000 units The company uses a traditional, volume-based product-costing system with manufacturing overhead applied on the basis of direct-labor dollars. The product costs have been computed as follows:
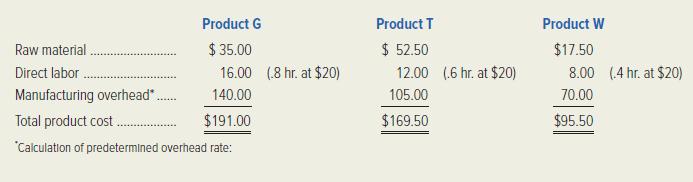

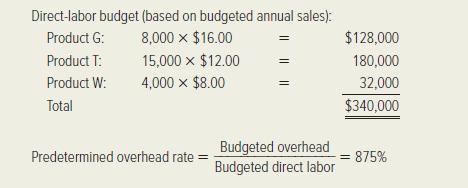
Gigabyte’s pricing method has been to set a target price equal to 150 percent of full product cost.
However, only the thingamajigs have been selling at their target price. The target and actual current prices for all three products are the following:

Gigabyte has been forced to lower the price of gismos in order to get orders. In contrast, Gigabyte has raised the price of whatchamacallits several times, but there has been no apparent loss of sales.
Gigabyte, Inc. has been under increasing pressure to reduce the price even further on gismos. In contrast, Gigabyte’s competitors do not seem to be interested in the market for whatchamacallits. Gigabyte apparently has this market to itself.
Required:
1. Is product G the company’s least profitable product?
2. Is product W a profitable product for Gigabyte, Inc.?
3. Comment on the reactions of Gigabyte’s competitors to the firm’s pricing strategy. What dangers does Gigabyte, Inc. face?
4. Gigabyte’s controller, Nan O’Second, recently attended a conference at which activity-based costing systems were discussed. She became convinced that such a system would help Gigabyte’s management to understand its product costs better. She got top management’s approval to design an activity-based costing system, and an ABC project team was formed. In stage one of the ABC project, each of the overhead items listed in the overhead budget was placed into its own activity cost pool. Then a cost driver was identified for each activity cost pool. Finally, the ABC project team compiled data showing the percentage of each cost driver that was consumed by each of Gigabyte’s product lines. These data are summarized as follows:
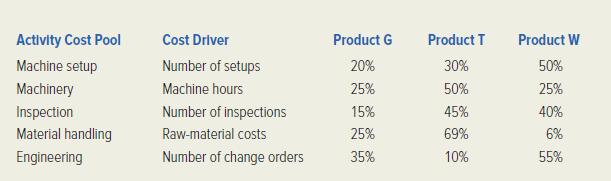
Show how the controller determined the percentages given above for raw-material costs. (Round to the nearest whole percent.) 5. Develop product costs for the three products on the basis of an activity-based costing system.
(Round to the nearest cent.)
6. Calculate a target price for each product, using Gigabyte’s pricing formula. Compare the new target prices with the current actual selling prices and previously reported product costs.
7. Build a spreadsheet: Construct an Excel spreadsheet to solve requirements (5) and (6) above.
Show how the solution will change if the inspection activity was divided among the three products in the following manner: product G, 20%; product T, 40%, and product W, 40%.
Step by Step Answer:

Managerial Accounting Creating Value In A Dynamic Business Environment
ISBN: 9781259569562
11th Edition
Authors: Ronald W.Helton, David E. Platt





