Two-Sample t Test Assuming Equal Variances The test scores on the same algebra test were recorded for
Question:
Two-Sample t Test Assuming Equal Variances The test scores on the same algebra test were recorded for nine students randomly selected from a classroom taught by teacher A and eight students randomly selected from a classroom taught by Teach- er B. Is there a difference in the average scores for students taught by these two teachers?
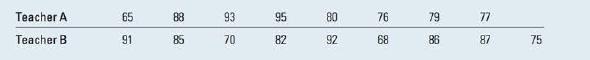
Enter the data into columns A and B of an Excel spreadsheet. 1. Use Data Data Analysis Descriptive Statistics or Statistical STDEV.S (STDEV in Excel 2007 and earlier versions) to find the standard deviations for the two samples, s = 9.913 and s = 8.800. Since the ratio of the two variances is s/s (less than 3), you are safe in assuming that the population variances are the same. 2. Select Data Data Analysis t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Equal Variances to generate the dialogue box in Figure 10.19(a). Highlight or type the Variable 1 Range and Variable 2 Range (the data in the first and second columns) into the first two boxes. In the box marked "Hypothesized Mean Difference" type 0 (since we are testing Ho: 0) and check "Labels" if necessary. 3. The default significance level is a = 0.05 in Excel. Change this significance level if necessary. Enter a cell location for the Output Range and click OK. The output will appear in the selected cell location, and should be adjusted using Format AutoFit Column Width on the Home tab in the Cells group while it is still highlighted. You can decrease the decimal accuracy if you like. using on the Home tab in the Number group. 4. The observed value of the test statistic t = -0.0337 is found in Figure 10.19
(b) in the row labeled "t Stat" followed by the one-tailed p-value "P(T
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Probability And Statistics
ISBN: 9780176509804
3rd Edition
Authors: William Mendenhall






