Para-xylene (p-xylene) is used as a raw material to make polyester fi bers. Billions of pounds are
Question:
Para-xylene (p-xylene) is used as a raw material to make polyester fi bers. Billions of pounds are produced every year. It is manufactured by reforming crude oil. p-Xylene must then be separated.
In this problem, we consider the fi nal step of the separation process where p-xylene is separated from its isomers, ortho-xylene and meta-xylene. All the isomers have similar physical properties. The latent heats and the boiling and melting points of the pure xylene isomers are reported below.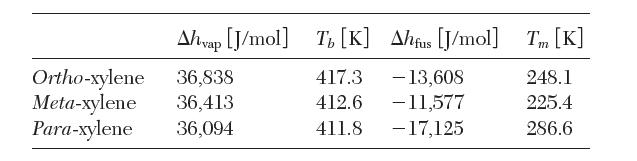
(a) From the data given, explain why crystallization of p-xylene from a liquid mixture of xylenes works better than distillation to separate p-xylene.
(b) Consider a liquid feed containing 1 mol ortho-, 2 mol meta-, and 1 mol para-xylene. You may assume that the liquid forms an ideal solution and neglect ![]() in your calculations. Additionally,assume that each species forms a completely immiscible solid phase.
in your calculations. Additionally,assume that each species forms a completely immiscible solid phase.
(i) Estimate the temperature at which the fi rst solid of each isomer will form, at the mole fraction that it exists in the liquid.
(ii) Estimate the temperature where half the p-xylene in the liquid has crystallized. Has either of the other isomers formed a solid at this temperature?
(iii) What is the lowest temperature that the system can have in which only p-xylene crystallizes?
What percentage of feed p-xylene has been separated?
(c) Instead, the liquid in part
(b) is vaporized at 140°C. The saturation pressures of the isomers at this temperature are as follows:
(i) What is the composition of vapor in equilibrium with the liquid of part (b).
(ii) Consider successive distillation “stages” where the vapor calculated in part
(i) is successively condensed and then evaporated. At total refl ux, how many stages would be required to reach a purity of 90% p-xylene?
Step by Step Answer:






