Increases in the mortgage interest rate increase the cost of owning a house and lower the demand
Question:
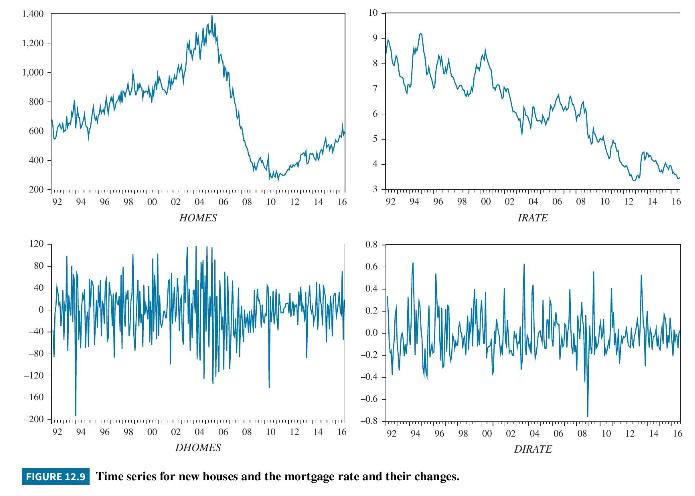
Increases in the mortgage interest rate increase the cost of owning a house and lower the demand for houses. In this question we investigate the properties of two time series that could be used to model this demand relationship: the number of new one-family houses sold in the U.S. (HOMES) and the 30 -year conventional mortgage rate (IRATE). These series, along with their changes, DHOMES and DIRATE, are plotted in Figure 12.9. The data are from January 1992 (1992M1) to September 2016 (2016M9). The units of measurement are thousands of new houses for HOMES and percentage points for IRATE.
Use the following test equation results to test for unit roots. In each case give the null and alternative hypotheses, and draw a conclusion. In all cases use a 5\% significance level. Based on the test results, describe how you would set up a model for the demand relationship. (In each model, the OLS standard errors do not reflect the true variance of the estimator \(\hat{\gamma}\) but, nevertheless, they can be used to construct the \(\tau\)-statistic.)

 g. In the following test equation the \(\hat{e}_{t}\) are the residuals from estimating the equation \(H O M E S_{t}=\) \(\beta_{1}+\beta_{2}\) IRATE \(_{t}+e_{t}\).
g. In the following test equation the \(\hat{e}_{t}\) are the residuals from estimating the equation \(H O M E S_{t}=\) \(\beta_{1}+\beta_{2}\) IRATE \(_{t}+e_{t}\).
\[
\begin{aligned}
& \widehat{\Delta \hat{e}_{t}}=-0.0191 \hat{e}_{t-1}-0.181 \Delta \hat{e}_{t-1} \\
& (\mathrm{se}) \quad(0.0117)
\end{aligned}
\]
h. In the following test equation the \(\hat{u}_{t}\) are the residuals from estimating the equation \(H O M E S_{t}=\) \(\beta_{1}+\delta_{t}+\beta_{2}\) IRATE \(_{t}+u_{t}\).
\[
\begin{aligned}
& \widehat{\Delta \hat{u}_{t}}=-0.0180 \hat{u}_{t-1}-0.208 \Delta \hat{u}_{t-1} \\
& (\mathrm{se}) \quad(0.0114)
\end{aligned}
\]
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Econometrics
ISBN: 9781118452271
5th Edition
Authors: R Carter Hill, William E Griffiths, Guay C Lim




