Question: Programming Exercise 8.12 writes a program for computing taxes using arrays. Design a class named Tax to contain the following instance data fields: For each
Programming Exercise 8.12 writes a program for computing taxes using arrays. Design a class named Tax to contain the following instance data fields:
For each filling status, there are six tax rates Each rate is applied to a certain amount of taxable income. For example, from the taxable income of $400,000 for a single filer, $8,350 is taxed at 10%, (33,950 - 8,350) at 15%, (82,250 - 33,950) at 25%, (171,550 - 82,550) at 28%, (372,550 - 82,250) at 33%, and (400,000 - 372,950) at 36%. The six rates are the same for all filling statuses, which can be represented in the following array:
double[] rate = (0.10, 0.15, 0.25, 0.28, 0.33, 0.35);
The brackets for each rate for all the filling staruses can be represented in two dimensional array a follows:
int[][] brackets = { ?{8350, 33950, 82250, 171550, 372950}, // Single filer {16700, 67900, 137C
Suppose the taxable income is $400,000 for single filers. The tax can be computed as follows:
![tax = brackets[0][0] * rates[0] + (brackets[0][1] brackets[0][0]) * rates[1] + (brackets[0][2]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/11/636a72c69462f_577636a72c17af72.jpg)
Listing
![brackets[0][1]) * rates[2] + (brackets[0][3] brackets[0][2]) * rates[3] + (brackets[0][4] brackets[0][3]) *](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/11/636a72c719564_583636a72c708e9b.jpg)
![rates[4] + (400000 brackets[0][4]) * rates[5] 1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/11/636a72c7b7e35_583636a72c7a7f33.jpg)
![class ComputeTax { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { // Create](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/11/636a72c870721_584636a72c8604f1.jpg)
? int filingStatus: One of the four tax-filing statuses: 0?single filer, 1? married filing jointly or qualifying widow(er), 2?married filing separately, and 3?head of household. Use the public static constants SINGLE_FILER (0), MARRIED_JOINTLY_OR_QUALIFYING_WIDOW(ER) (1), MARRIED_SEPARATELY (2), HEAD_OF_HOUSEHOLD (3) to represent the statuses.??int[][] brackets: Stores the tax brackets for each filing status.??double[] rates: Stores the tax rates for each bracket.??double taxableIncome: Stores the taxable income.Provide the getter and setter methods for each data field and the getTax() method that returns the tax. Also provide a no-arg constructor and the constructor Tax(filingStatus, brackets, rates, taxableIncome).Draw the UML diagram for the class and then implement the class. Write a test program that uses the Tax class to print the 2001 and 2009 tax tables for taxable income from $50,000 to $60,000 with intervals of $1,000 for all four statuses.The tax rates for the year 2009 were given in Table 3.2. The tax rates for 2001 are shown in Table 10.1.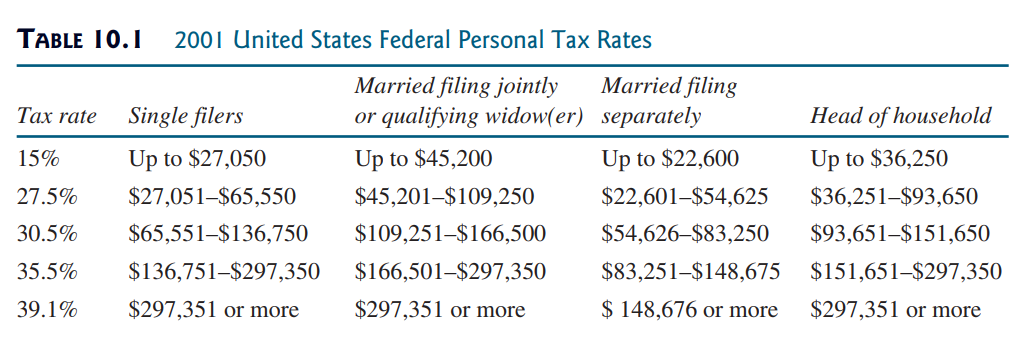
Marginal Tax Rate |
Single |
Married Filing Jointly or Qualifying Widow(er) |
Married Filing Separately |
Head of Household |
10% |
$0 ? $8,350 |
$0 ? $16,700 |
$0 ? $8,350 |
$0 ? $11,950 |
15% |
$8,351 ? $33,950 |
$16,701 ? $67,900 |
$8,351 ? $33,950 |
$11,951 ? $45,500 |
25% |
$33,951 ? $82,250 |
$67,901 ? $137,050 |
$33,951 ? $68,525 |
$45,501 ? $117,450 |
28% |
$82,251 ? $171,550 |
$137,051 ? $208,850 |
$68,526 ? $104,425 |
$117,451 ? $190,200 |
33% |
$171,551 ? $372,950 |
$208,851 ? $372,950 |
$104,426 ? $186,475 |
$190,201 ? $372,950 |
35% |
$372,951+ |
$372,951+ |
$186,476+ |
$372,951+ |
tax = brackets[0][0] * rates[0] + (brackets[0][1] brackets[0][0]) * rates[1] + (brackets[0][2] brackets[0][1]) * rates[2] + (brackets[0][3] brackets[0][2]) * rates[3] + (brackets[0][4] brackets[0][3]) * rates[4] + (400000 brackets[0][4]) * rates[5] 1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class ComputeTax { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a Scanner Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 5 // Prompt the user to enter filing status System.out.print("(0-single filer, 1-married jointly or "qualifying widow(er), 2-married separately, 3-head of "household) Enter the filing status: "); 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int status - input.nextInt(); // Prompt the user to enter taxable income System.out.print("Enter the taxable income: "); double income = input.nextDouble(); // Compute tax double tax - 0; if (status == 0) { // Compute tax for single filers if (income
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Program Plan 1 Create a class Tax 2 Declare the variables Int filingStatus Filing status public static final int SINGLEFILER 0 Single filer public sta... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


