Product cost calculation and costs for decision-making Shown below is next year's budget for an engineer- ing
Question:
Product cost calculation and costs for decision-making Shown below is next year's budget for an engineer- ing company manufacturing two different products in two production departments, namely a machine shop and an assembly department. A stores depart- ment is responsible for storing and issuing materi- als.
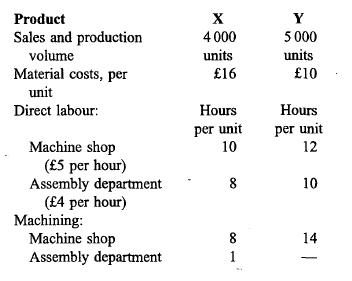
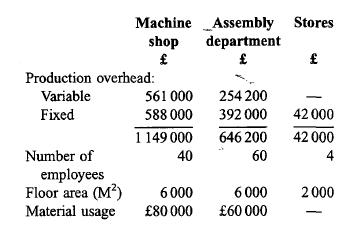
Maximum practical capacity is 140 000 machine hours for the machine shop and additional capacity for the assembly department is easily obtainable. Machine hour capacity cannot be increased over the next year. Fixed overheads are common and unavoidable to all alternatives and will remain unchanged irrespective of the level of production capacity. Overheads are charged to production on the basis of budgeted activity, and selling prices are determined on a cost-plus basis by adding 20 per cent to total cost.
(a) You are required to establish an appropriate overhead absorption rate for each production department and calculate the selling price for each unit using the company's cost-plus pricing method. You must clearly state and briefly justify the methods of overhead absorption used. (9 marks)
(b) In addition to the above data, two special orders have been received, outside the normal run of business, and not provided for in the budget. They are as follows: (i) an order for 1000 units of product X from Regan plc offering to pay 200 per unit for them; (ii) a contract to supply 500 units per month of product X from Thatcher plc for 12 months at a price per unit of 220. You are required to set out the considerations which the management of the engineering company should take into account when deciding whether to accept each of these orders, and advise the company as far as you are able on the basis of the information given. (10 marks)
Step by Step Answer:






