Advanced: Pricing decisions under conditions of uncertainty (a) Allegro Finishes Ltd is about to launch an improved
Question:
Advanced: Pricing decisions under conditions of uncertainty
(a) Allegro Finishes Ltd is about to launch an improved version of its major product - a pocket size chess computer - onto the market. Sales of the original model (at £65 per unit) have been at the rate of 50 000 per annum but it is now planned to withdraw this model and the company is now deciding on its produc¬ tion plans and pricing policy.
The standard variable cost of the new model will be £50 which is the same as that of the old, but the company intends to increase the selling price ‘to recover the research and development expenditure that has been incurred’. The research and development costs of the improved model are estimated at £750 000 and the intention is that these should be written off over 3 years. Additionally there are annual fixed overheads of approximately £800 000 allocated to this product line.
The sales director has estimated the maxi¬ mum annual demand figures that would obtain at three alternative selling prices. These are as follows: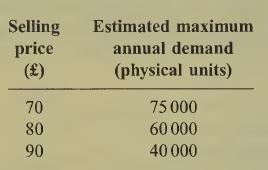
You are required to prepare a cost-volume- profit chart that would assist the management to choose a selling price and the level of output at which to operate. Identify the best price and the best level of output. Outline briefly any reservations that you have with this approach. (5 marks)
(b) With the facts as stated for part (a), now assume the sales director is considering a more sophisticated approach to the problem. He has estimated, for each selling price, an optimistic, a pessimistic and a most likely demand figure and associated probabilities for each of these. For the £90 price the estimates are: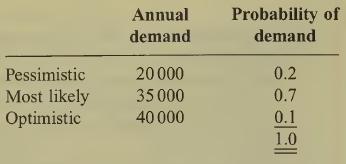
On the cost side, it is clear that the standard unit variable cost of £50 is an ‘ideal’ which has rarely been achieved in practice. An analysis of the past 20 months shows that the following pattern of variable cost variances (per unit of output) has arisen: an adverse variance of around £10 arose on 4 occasions, an adverse variance of around £5 arose on 14 occasions and a variance of around 0 arose on 2 occa¬ sions.
There is no reason to think that the pattern for the improved model will differ signifi¬ cantly from this or that these variances are dependent upon the actual demand level.
From the above, calculate the expected annual profit for a selling price of £90.
(6 marks)
(c) A tabular summary of the result of an analysis of the data for the other two selling prices (£70 and £80) is as follows: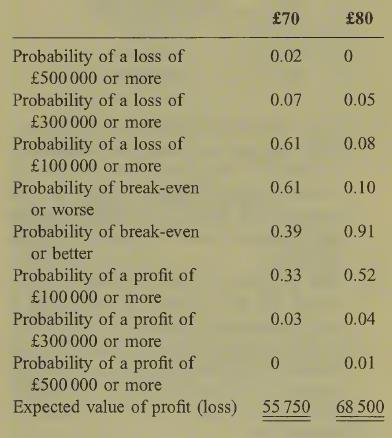
You are required to compare your calculations in part
(b) with the above figures and to write a short memo to the sales director outlining your advice and commenting on the use of subjective discrete probability distributions in problems of this type. (9 marks)
(d) Assume that there is a 10% increase in the fixed overheads allocated to this product line and a decision to write off the research and development costs in one year instead of over 3 years. Indicate the general effect that this would have on your analysis of the problem.
Step by Step Answer:






