After attending a seminar on measuring customer profitability, Mason Ford decided to examine Olson Optics customers to
Question:
After attending a seminar on measuring customer profitability, Mason Ford decided to examine Olson Optics’ customers to determine if the company truly knew how profitable its customers were.
Olson Optics already uses an activity-based costing system to determine the product cost of its two products: RF3O and LF4S. Each RF3O sells for $16.00 and requires $7.60 in direct materials and $5.00 in direct labor. Each LF45 sells for $50.00 and requires $16.40 in direct materials and $14.80 in direct labor. The following table provides cost and activity information for manufacturing overhead for the two products.
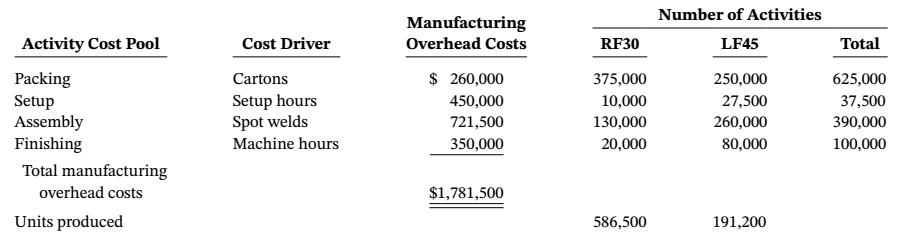
Based on what Ford learned at seminar, he has gathered the following information about costumer support activities.
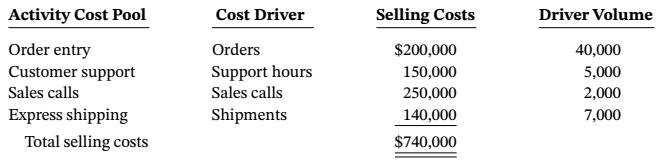
Ford wants to apply his new profitability analysis techniques to Infrared Technologies, a company he believes is representative of Olson’s average customer. Information about Infrared’s account activity is as follows.
RF3O purchases . . . . . . . . . . . 10,000 units
LF45 purchases . . . . . . . . . . . 3,000 units
Orders placed . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Customer support . . . . . . . . . . . 350 hours
Sales calls 2 . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Express shipments . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Required
a. Calculate the activity-based product cost for RF3O and LF45.
b. Calculate the cost pool rates for Olson’s customer service activities.
c. Calculate the gross profit, customer net profit, and customer profit margin for Infrared Technologies. Round customer profit margin to 1 decimal place.
d. Is Infrared Technologies a profitable customer? Why or why not?
e. What actions could Ford take to increase Infrared Technologies’ profitability? Should these actions be applied to all of Olson’s customers?
Step by Step Answer:






