Waves Galore, Inc. manufactures hair curlers and blow-dryers. The handheld hair curler is Waves Galore's high volume
Question:
Waves Galore, Inc. manufactures hair curlers and blow-dryers. The handheld hair curler is Waves Galore's high volume product ( 80,000 units annually). It is a "large barrel," 20-watt, triple-heat appliance designed to appeal to the teenage market segment with its glow-in-the-dark handle. The handheld blow-dryer is Waves Galore's lower-volume product ( 40,000 units annually). It is a three-speed, 2,000 watt appliance with a "cool setting" and a removable filter. It also is designed for the teen market.
Both products require one hour of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are \(120,000,(80,000+40,000)\). Expected annual manufacturing overhead is \(\$ 438,000\). Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is \(\$ 3.65\) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is \(\$ 5.25\) for the hair curler and \(\$ 9.75\) for the blowdryer. The direct labor cost is \(\$ 8.00\) per unit for the hair curler and the blow-dryer.
Waves Galore purchases most of the parts from suppliers and assembles the finished product at its Fargo, North Dakota plant. It recently adopted activity-based costing, which after this year-end will totally replace its traditional direct labor-based cost accounting system. Waves Galore has identified the following six activity cost pools and related cost drivers and has assembled the following information.
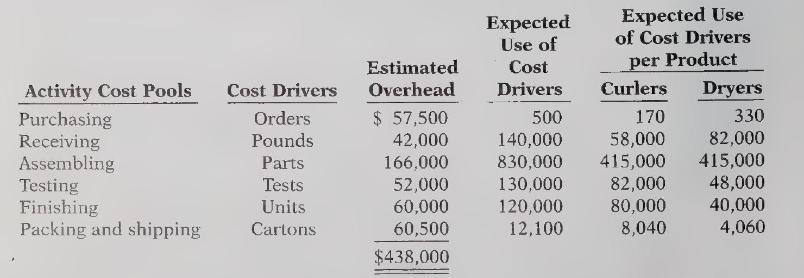
Instructions:
(a) Under traditional product costing, compute the total unit cost of each product. Prepare a simple comparative schedule of the individual costs by product (similar to Illustration 17-4).
(b) Under ABC, prepare a schedule showing the computations of the activity-based overhead rates per cost driver. (Round to the nearest cent.)
(c) Prepare a schedule assigning each activity's overhead cost pool to each product based on the use of cost drivers. (Include a computation of overhead cost per unit, rounding to the nearest cent.)
(d) Compute the total cost per unit for each product under ABC.
(e) Classify each of the activities as a value-added activity or a non-value-added activity.
(f) Comment on (1) the comparative overhead cost per unit for the two products under \(A B C\), and (2) the comparative total costs per unit under traditional costing and \(A B C\).
Step by Step Answer:

Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making
ISBN: 9780470377857
3rd Edition
Authors: Paul D. Kimmel





