Alpha and Beta in Technical Problem 15 repeat their pricing decision on the first day of every
Question:
Alpha and Beta in Technical Problem 15 repeat their pricing decision on the first day of every month. Suppose they have been cooperating for the past few months, but now the manager at Beta is trying to decide whether to cheat or to continue cooperating. Beta?s manager believes Beta can get away with cheating for two months, but would be punished for the next two months after cheating. After punishment, Beta?s manager expects the two firms would return to cooperation. Beta?s manager uses a discount rate of 2 percent per month for computing present values.a. What is the monthly (un-discounted) gain to Beta from cheating? What is the present value of the benefit from cheating?b. What is the monthly (un-discounted) cost of punishment to Beta? What is the present value of the cost of cheating?c. Will Beta cooperate or cheat? Explain.d. Suppose Beta discounts future benefits and costs at a rate of 30 percent per week. Will Beta choose cooperation or cheating?
Data From Problem 15
Alpha and Beta, two oligopoly rivals in a duopoly market, choose prices of their products on the first day of the month. The following payoff table shows their monthly payoffs resulting from the pricing decisions they can make.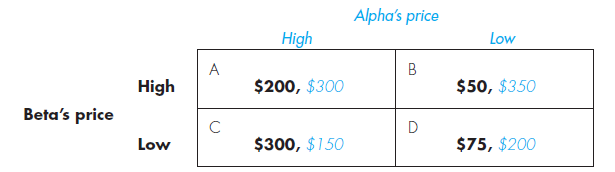
Depending upon the context, the discount rate has two different definitions and usages. First, the discount rate refers to the interest rate charged to the commercial banks and other financial institutions for the loans they take from the Federal...
Step by Step Answer:

Managerial Economics Foundations of Business Analysis and Strategy
ISBN: 978-0078021909
12th edition
Authors: Christopher Thomas, S. Charles Maurice





