Repeat the comparison in Question 3 of Chapter 10, except this time leave correlations constant (i.e. 0%
Question:
Repeat the comparison in Question 3 of Chapter 10, except this time leave correlations constant (i.e. 0% between spot FX and interest rates). Instead, increase both interest rates vols to 1%. Next decrease both interest rates vols to 0%. How do forward FX variances compare?
Question 3
Use the same parameters as in Question 2 except where specified otherwise. Compute the 10-year forward starting volatilities for expiries 1y, 2y,..., 10y. Now, increase the domestic-spot correlation to 20% and bootstrap spot FX vols so that forward FX variances for expiries 1y, 2y,..., 20y are preserved. Again, compute the 10-year forward starting volatilities above. How do they compare? Try the same instead by increasing the foreign-spot correlation to 20%.
Question 2
Consider the same parameterisation as in Question 1 but to be more specific, say the HJM processes correspond to a Hull-White model with constant vol of 0.7% and mean reversion speed of 2%. Take lognormal spot FX vol as 15%. The correlation for the domestic-foreign rates is 30% and other correlations are 0%. Using the formula for forward vol in Section 10.1.1, determine how much of forward variance comes from the interest rates component and how much from the spot component for forward starting times 1y, 5y, 10y and expiries 1y, 5y,10y, 20y, 30y.
Question 1
Consider the following parameterisation based on Gaussian interest rates and lognormal spot FX : dSt = (rt – rƒt) Stdt + 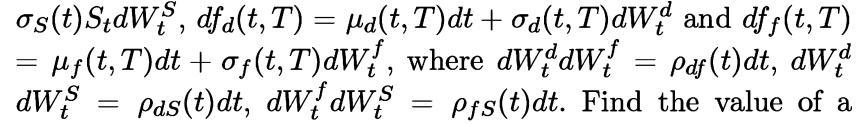 quanto Libor rate, i.e. where the Libor rate LT (set at time T, with accrual fraction Ƭ and paid at time T + Ƭ) is in the foreign currency but paid in the domestic currency without conversion at the FX rate.
quanto Libor rate, i.e. where the Libor rate LT (set at time T, with accrual fraction Ƭ and paid at time T + Ƭ) is in the foreign currency but paid in the domestic currency without conversion at the FX rate.
Section 10.1.1


Step by Step Answer:






