Question: Use the infinite series in the Problem 13 derive the derivative identities ((6.59)) and ((6.60)) : a. (frac{d}{d x}left[x^{n} J_{n}(x) ight]=x^{n} J_{n-1}(x)). b. (frac{d}{d x}left[x^{-n}
Use the infinite series in the Problem 13 derive the derivative identities \((6.59)\) and \((6.60)\) :
a. \(\frac{d}{d x}\left[x^{n} J_{n}(x)\right]=x^{n} J_{n-1}(x)\).
b. \(\frac{d}{d x}\left[x^{-n} J_{n}(x)\right]=-x^{-n} J_{n+1}(x)\).
Data from Problem 13
A solution of Bessel's equation, \(x^{2} y^{\prime \prime}+x y^{\prime}+\left(x^{2}-n^{2}\right) y=0\), can be found using the guess \(y(x)=\sum_{j=0}^{\infty} a_{j} x^{j+n}\). One obtains the recurrence relation \(a_{j}=\frac{-1}{j(2 n+j)} a_{j-2}\). Show that for \(a_{0}=\left(n!2^{n}\right)^{-1}\), we get the Bessel function of the first kind of order \(n\) from the even values \(j=2 k\) :
\[J_{n}(x)=\sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{(-1)^{k}}{k!(n+k)!}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)^{n+2 k}\]
Data from 6.59
![d [x Jp(x)] dx xJp-1(x).](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1716/5/3/4/17266503b9ce8f971716577339284.jpg)
Data from 6.60
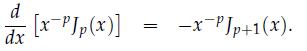
d [x Jp(x)] dx xJp-1(x).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


