Question: In the PCB described in Problem 9.63, it is desired to reduce the displacement transmissibility to a value of 0.25. If the chassis mass is
In the PCB described in Problem 9.63, it is desired to reduce the displacement transmissibility to a value of 0.25. If the chassis mass is 50 percent of the mass of the PCB, determine the necessary stiffness \((k)\) and damping constant \((c)\) of the isolator if the damping ratio of the isolator is required to be 0.01.
Data From Problem 9.63:-
A printed circuit board (PCB), made of fiber reinforced plastic composite material, is attached to a chassis that is attached to a motor vibrating at a speed of \(3000 \mathrm{rpm}\). The PCB can be modeled as a fixed-fixed beam, similar to the one shown in Fig. 9.27, with a length (l) \(20 \mathrm{~cm}\), width \((w) 16 \mathrm{~cm}\), thickness \((t) 0.2\mathrm{~cm}\), mass (m) \(1.0 \mathrm{~kg}\), and Young's modulus \((E)\) \(12.5 \times 10^{9} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{m}^{2}\). Determine the following:
a. Stiffness of the PCB
b. Natural frequency of the PCB
c. Displacement transmissibility of the PCB Assume the damping to be negligible.
Figure 9.27:-
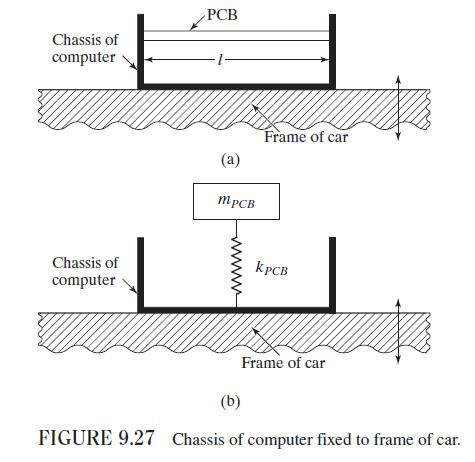
Chassis of computer PCB Chassis of computer (a) MPCB Frame of car KPCB (b) Frame of car FIGURE 9.27 Chassis of computer fixed to frame of car.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


