Question: CP8.8 pendulum on a moving base, as shown in Figure Consider the problem of controlling an inverted CP8.8(a). The transfer function of the system is
CP8.8 pendulum on a moving base, as shown in Figure Consider the problem of controlling an inverted CP8.8(a). The transfer function of the system is
![]()
The design objective is to balance the pendulum
(i.e., θ( )t ≈ 0 ) in the presence of disturbance inputs.
A block diagram representation of the system is depicted in Figure CP8.8(b). Let Ms = 10kg, Mb = 100 kg, = 1m, 9.81m/s2 a = 5, and b = 10.
The design specifications, based on a unit step distur
bance, are as follows:
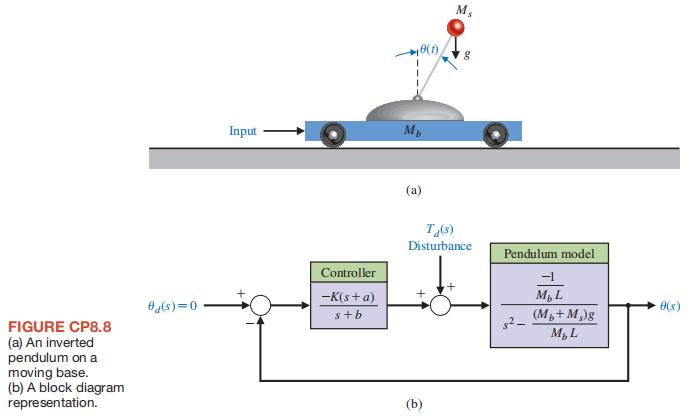
1. settling time (with a 2% criterion) of Ts ≤ 10 s,
2. percent overshoot of P O. . ≤ 40%, and
3. steady-state tracking error less than 0.1° in the presence of the disturbance.
Develop a set of interactive m-file scripts to aid in the control system design. The first script should accom
plish at least the following:
1. Compute the closed-loop transfer function from the disturbance to the output with K as an adjust
able parameter.
2. Draw the Bode plot of the closed-loop system.
3. Automatically compute and output Mpω and ωr.
As an intermediate step, use Mpω and ωr and Equations (8.36) and (8.37) in Section 8.2 to estimate
ζ and ωn. The second script should at least estimate the settling time and percent overshoot using ζ and
ωn as input variables.
If the performance specifications are not satis
fied, change K and iterate on the design using the first two scripts. After completion of the first two steps, the final step is to test the design by simulation. The func
tions of the third script are as follows:
1. plot the response, θ( )t , to a unit step disturbance with K as an adjustable parameter, and
2. label the plot appropriately.
Utilizing the interactive scripts, design the controller to meet the specifications using frequency response Bode methods. To start the design process, use analytic methods to compute the minimum value of K to meet the steady-state tracking error specification. Use the minimum K as the first guess in the design iteration.
-1/(ML) G(s)= s2 (M+Ms)g (M,L)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


