Question: CP9.7 An engineering laboratory has presented a plan to operate an Earth-orbiting satellite that is to be controlled from a ground station. A block diagram
CP9.7 An engineering laboratory has presented a plan to operate an Earth-orbiting satellite that is to be controlled from a ground station. A block diagram of the proposed system is shown in Figure CP9.7. 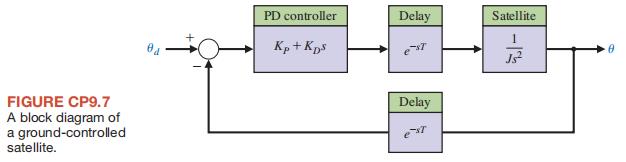
It takes T seconds for a signal to reach the space
craft from the ground station and the identical delay for a return signal. The proposed ground-based controller is a proportional-derivative (PD) control
ler, where
G s c P ( ) = + K KDs.
(a) Assume no transmission time delay (i.e., T = 0), and design the controller to the following spec
ifications: (1) percent overshoot P O. . ≤ 20% to a unit step input and (2) time to peak Tp ≤ 30 s.
(b) Compute the phase margin with the controller in the loop but assuming a zero transmission time delay. Estimate the amount of allowable time delay for a stable system from the phase margin calculation.
(c) Using a second-order Padé approximation to the time delay, determine the maximum allowable delay Tmax for system stability by developing a m-file script that employs the pade function and computes the closed-loop system poles as a func
tion of the time delay T. Compare your answer with the one obtained in part (b).
FIGURE CP9.7 A block diagram of a ground-controlled satellite. PD controller Kp+KDS Delay Satellite Delay -13 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


