Question: Application 6.3 modeled a meson (a quark-antiquark pair) as a finite dipole placed at the center of a spherical cavity with radius R and unit
Application 6.3 modeled a meson (a quark-antiquark pair) as a finite dipole placed at the center of a spherical cavity with radius R and unit dielectric constant scooped out of an infinite medium with dielectric constant κ → 0. For this problem, we replace the finite dipole by a point dipole p.

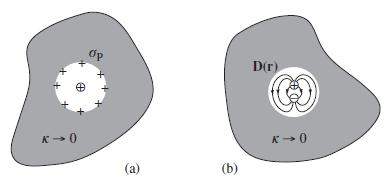
(a) Find D and E everywhere for finite κ.
(b) Confirm the statements made in the Application regarding D and UE when κ = 0. Assume a cutoff distance a
Application 6.3 A Classical Model for Quark Confinement Quantum chromodynamics (QCD) assigns a "color" degree of freedom to quarks. For some purposes, the QCD vacuum may be regarded as a dielectric medium for color charge with a vanishingly small dielectric constant K. Because < 1, this fictitious dielectric medium "anti-screens" free charge in the sense that (6.43) tells us that the polarization charge has the same sign as the free charge, thereby enhancing the effect of the latter. On the other hand, Coulomb repulsion prevents the free charge and the polarization charge from getting too close together. This suggests that a tiny sphere with color charge q and radius a digs itself a vacuum hole of radius R in the dielectric. This is indicated in both panels of Figure 6.14.
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b If we orient p along the zaxis the dipole makes a contribution p47o... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


