For the data of the previous exercise, now consider testing the hypothesis of equal population variances. a.
Question:
For the data of the previous exercise, now consider testing the hypothesis of equal population variances.
a. Carry out a two-tailed test using the method of Section 10.5. Recall that this method requires the data to be normal, and the method is sensitive to departures from normality. Check the data for normality to see if the F test is justified.
b. Carry out a two-tailed permutation test for the hypothesis of equal population variances (or standard deviations). Why does it not matter whether you use variances or standard deviations?
c. Compare the two results and summarize your conclusions.
Data From previous Exercises
A student project by Heather Kral studied students on “lifestyle floors” of a dormitory in comparison to students on other floors. On a lifestyle floor the students share a common major, and there are a faculty coordinator and resident assistant from that department. Here are the GPAs of 30 students on lifestyle floors (L) and 30 students on other floors (N):
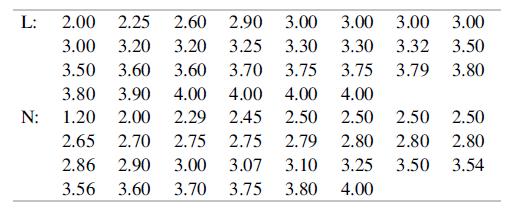
Notice that the lifestyle GPAs have a large number of repeats and the distribution is skewed, so there is some question about normality.
Step by Step Answer:

Modern Mathematical Statistics With Applications
ISBN: 9783030551551
3rd Edition
Authors: Jay L. Devore, Kenneth N. Berk, Matthew A. Carlton





