Question: Evaluate the formula for the Gauss-Bonnet theorem in Box 28.3 for a 2-sphere and show that this leads to the usual relation for the area
Evaluate the formula for the Gauss-Bonnet theorem in Box 28.3 for a 2-sphere and show that this leads to the usual relation for the area of a sphere. The local curvature for a 2-surface is the Gaussian curvature.
Data from Box 28.3
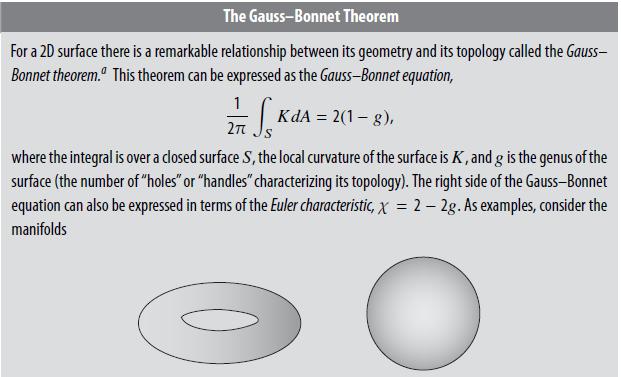

The Gauss-Bonnet Theorem For a 2D surface there is a remarkable relationship between its geometry and its topology called the Gauss- Bonnet theorem." This theorem can be expressed as the Gauss-Bonnet equation, 1 KdA = 2(1-g), 2 where the integral is over a closed surface S, the local curvature of the surface is K, and g is the genus of the surface (the number of "holes" or "handles" characterizing its topology). The right side of the Gauss-Bonnet equation can also be expressed in terms of the Euler characteristic, X = 2-2g. As examples, consider the manifolds
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The problem involves applying the GaussBonnet theorem to a 2sphere and showing that it leads to the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


