It is not an easy matter to assign particular functions to specific components of the basal lamina,
Question:
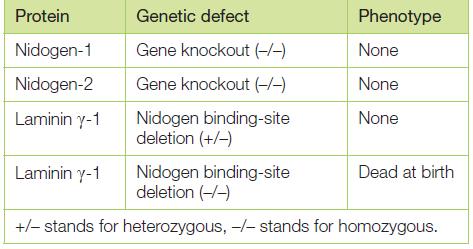
It is not an easy matter to assign particular functions to specific components of the basal lamina, since the overall structure is a complicated composite material with both mechanical and signaling properties. Nidogen, for example, cross-links two central components of the basal lamina by binding to the laminin γ-1 chain and to type IV collagen. Given such a key role, it was surprising that mice with a homozygous knockout of the gene for nidogen-1 were entirely healthy, with no abnormal phenotype. Similarly, mice homozygous for a knockout of the gene for nidogen-2 also appeared completely normal. By contrast, mice that were homozygous for a defined mutation in the gene for laminin γ-1, which eliminated just the binding site for nidogen, died at birth with severe defects in lung and kidney formation. The mutant portion of the laminin γ-1 chain is thought to have no other function than to bind nidogen, and does not affect laminin structure or its ability to assemble into the basal lamina. How would you explain these genetic observations, which are summarized in Table Q19–1? What would you predict would be the phenotype of a mouse that was homozygous for knockouts of both nidogen genes?
Table Q19-1
Step by Step Answer:

Molecular Biology Of The Cell
ISBN: 9780815344322
6th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter





