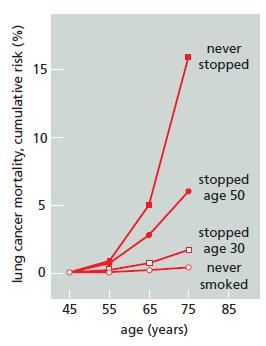
Mortality due to lung cancer was followed in groups of males in the United Kingdom for 50
Question:
Mortality due to lung cancer was followed in groups of males in the United Kingdom for 50 years. Figure Q20–1 shows the cumulative risk of dying from lung cancer as a function of age and smoking habits for four groups of males: those who never smoked, those who stopped at age 30, those who stopped at age 50, and those who continued to smoke. These data show clearly that individuals can substantially reduce their cumulative risk of dying from lung cancer by stopping smoking. What do you suppose is the biological basis for this observation?
Figure Q20-1
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Molecular Biology Of The Cell
ISBN: 9780815344322
6th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Question Posted:





