Consider the partial differential equation subject to c(0, t) = 0 and We will consider three cases:
Question:
Consider the partial differential equation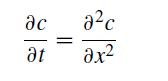 subject to c(0, t) = 0 and
subject to c(0, t) = 0 and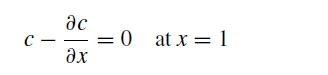
We will consider three cases: c(x, 0) = 1, c(x, 0) = x and c(x, 0) = x2. Note that the second initial condition is a steady state solution to the PDE.
(a) Use finite differences and the method of lines to recast this problem as a system of ordinary differential equations. Be sure to specify the initial conditions on each equation.
(b) Recast the result in part (a) as a system of algebraic equations to compute ci(k+1) using implicit Euler.
(c) Write a MATLAB program that integrates the solution to part (b). For c(x, 0) = x, make a plot of the difference between the solution at t = 0.01 and t = 0. Is this what you expect? For the other initial conditions, make a plot of the concentration at t = 0, 0.0005, 0.01, 0.05, 0.07, and 0.2. Be sure to include a legend.
Step by Step Answer:

Numerical Methods With Chemical Engineering Applications
ISBN: 9781107135116
1st Edition
Authors: Kevin D. Dorfman, Prodromos Daoutidis




