The Zoom automobile company28 is planning capacities and configurations of 3 plants to produce 4 new models
Question:
The Zoom automobile company28 is planning capacities and configurations of 3 plants to produce 4 new models being introduced for the coming market cycle. The first part of the following table shows the configuration options available at each plant, along with the implied capacities (in thousands of cars) and (fixed)
changeover costs (in $ million). Option 1 of each plant is the current facility configuration making changeover cost = 0. Different configurations at the plants imply different mixes of models that can be manufactured there. Part two of the table adds the marginal production cost per thousand units of the products eligible for manufacture at the site given the chosen configuration.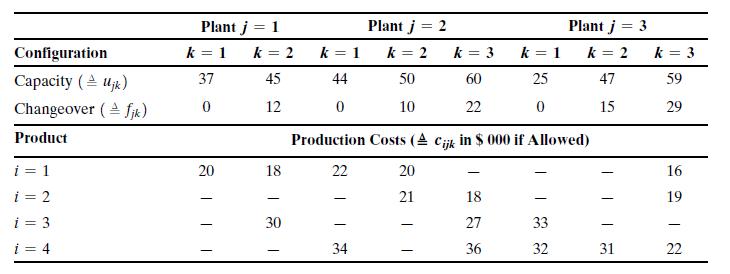
Exactly one configuration must be chosen for each plant well in advance, but demands and market prices that will arise for units produced are uncertain until later. The next table shows 4 scenarios for available demands and prices applicable for the entire market cycle. Estimated probabilities for the scenarios are p1s2 = 0.15, 0.30, 0.35, and 0.20 respectively.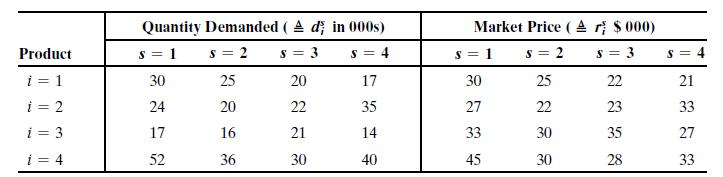
(a) Explain why Zoom’s capacity planning task can be formulated as a two-stage mixed-integer stochastic program with with recourse (definition 4.18 ) taking production capacity decisions in Stage 1 and determining implied scenario production and sales in Stage 2.
(b) Using parameters defined above and decision variables yjk ! 1 if plant j is placed in configuration k1= 0 otherwise2, and xijk 1s2 Ú 0 ! the quantitiy (in thousands)
of models i produced and sold from plant j if it is placed in configuration k under scenario s, formulate a two-stage mixed-integer stochastic program in extensive form (Figure 4.4) to choose a maximum expected profit plan for Zoom.
(c) Use class optimization software to solve your model of
(b) and describe the plan that results.
Step by Step Answer:






