A compound microscope consists of two converging lenses, the objective lens and the eyepiece lens, positioned on
Question:
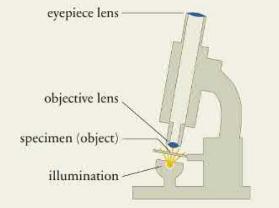
A compound microscope consists of two converging lenses, the objective lens and the eyepiece lens, positioned on a common optical axis (Figure 33.47). The objective lens is positioned to form a real, highly magnified image 1 of the sample being examined, and the eyepiece lens is positioned to form a virtual, further magnified image 2 of image 1 . It is image 2 that the user sees. A knob on the microscope allows the user to move the objective lens upward and downward to change both the sample-objective lens distance and the distance between the two lenses.
(a) How must the sample and the two lenses be positioned relative to one another so that the user sees a highly magnified, virtual image of the sample?
(b) What is the overall magnification produced by the microscope?
Data from Figure 33.47
Step by Step Answer:






