Cesium chloride ((mathrm{CsCl})) is a crystalline salt that forms in a cubic lattice structure, which you can
Question:
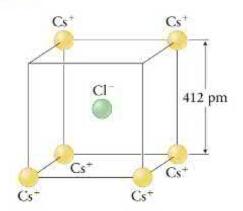
Cesium chloride \((\mathrm{CsCl})\) is a crystalline salt that forms in a cubic lattice structure, which you can imagine as a cube with \(\mathrm{Cs}^{+}\)ions at the eight corners and \(\mathrm{Cl}^{-}\)ion at the center. The edge length of the cube is \(412 \mathrm{pm}\). Suppose that at the edge of a crystal, two cesium atoms have been stripped from adjacent corners of a cube, as shown in Figure P22.55. What is the vector sum of the electric forces exerted on the chloride ion by the six \(\mathrm{Cs}^{+}\)ions remaining in the cube?
Data from Figure P22.55
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





