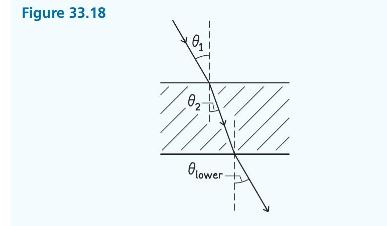
Question: We found in Example 33.3 that a light ray is refracted twice when it passes completely through a slab of transparent material (see Figure 33.18).
We found in Example 33.3 that a light ray is refracted twice when it passes completely through a slab of transparent material (see Figure 33.18). The result of these two refractions is that the exiting ray is shifted sideways relative to the entering ray. Let the slab be in air with an index of refraction \(n_{1}=1\).
(a) Derive an expression for the distance (perpendicular to the ray) over which the ray is shifted sideways for an angle of incidence \(\theta_{1}\), slab thickness \(d\), and slab index of refraction \(n_{2}\).
(b) Calculate the value of the shift for \(\theta_{1}=30^{\circ}, n_{2}=1.5\), and \(d=0.010 \mathrm{~m}\).
Data from Example 33.3
Consider a light ray incident on a parallel-sided slab of glass surrounded by air, as shown in Figure 33.17a. The ray travels all the way through the slab and emerges into air on the other side. In what direction does the ray emerge?
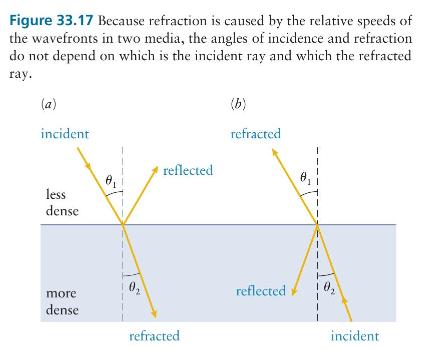
Figure 33.18 82 lower
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


