Question:
Calculate ΔĤ for each of the following processes. In each case, restate your result as a specific enthalpy relative to a reference state. [The solution—which you should verify—and the restatement for Part (a) are given as an illustration.] Assume that the process pressures are low enough for Ĥ to be considered independent of pressure, so that the formulas of Table B.2 (which strictly apply at 1 atm) can be used.
(a) CH3COCH3(l, 15°C) → CH3COCH3(l, 55°C).
Solution: ΔĤ = 5.180 kJ/mol
The specific enthalpy of liquid acetone at 55°C relative to liquid acetone at 15°C is 5.180 kJ/mol.
(b) n-C6H14(l, 25°C) → n-C6H14(l, 80°C)
(c) n-C6H14(v, 500°C) → n-C6H14(v, 0°C).
(Make statements about both the specific enthalpy of hexane vapor at 500°C relative to hexane vapor at 0°C and the specific enthalpy of hexane vapor at 0°C relative to hexane vapor at 500°C.)
Table B.2
![TABLE B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol·K)] = a + bT + cT + dT Form 2: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol-K)] = a + bT + cT? Example: (C,)acetone(e) = 0.07196 + (20.10 x 10-$)r - (12.78 x 10-8)7? + (34.76 x 10-12)Tr*, where T is in °C. %3D](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1590/0/5/6/4075ec655d7a186e1590056399297.jpg)
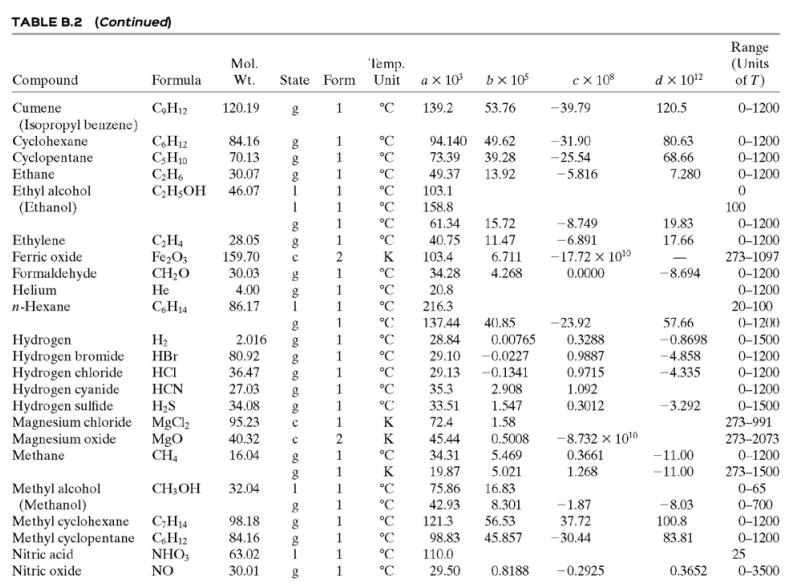
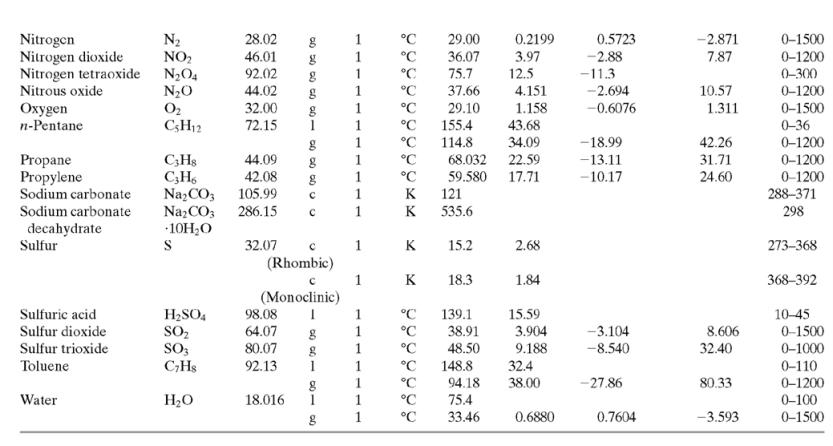
Transcribed Image Text:
TABLE B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol·K)] = a + bT + cT + dT Form 2: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol-K)] = a + bT + cT? Example: (C,)acetone(e) = 0.07196 + (20.10 x 10-$)r - (12.78 x 10-8)7? + (34.76 x 10-12)Tr*, where T is in °C. %3D Note: The formulas for gases are strictly applicable at pressures low enough for the ideal-gas equation of state to apply. Range (Units of T) Mol. Temp. State Form Unit ax 10 b x 10 ex 10 d x 1012 Compound Formula Wt. CH;COCH; 58.08 1 °C 123.0 -30-60 18.6 20.10 6.053 0.4147 Acetone °C 34.76 71.96 42.43 28.94 -12.78 -5.033 0.3191 0-1200 0-1200 0-1500 C;H2 26.04 29.0 °C Acetylene Air 18.20 -1.965 1.965 1. 28.09 0.1965 0.4799 273-1800 Ammonia NH, 17.03 °C 35.15 2.954 0.4421 -6.686 0-1200 Ammonium sulfate Benzene (NH4)2SO4 132.15 C,H, 1 215.9 275-328 126.5 74.06 78.11 1 °C 23.4 32.95 6-67 0-1200 1 -25.20 77.57 CH10 CH10 CHs CaC2 CACO, Ca(OH)2 Isobutane 58.12 89.46 49.87 30.13 27.88 -18.91 0-1200 0-1200 0-1200 n-Butane 58.12 92.30 -15.47 34.98 25.64 50.50 Isobutene Calcium carbide Calcium carbonate 56.10 1 82.88 -17.27 -8.66 x 1010 -12.87 x 1010 64.10 K 68.62 1.19 298-720 100.09 K 82.34 4.975 273-1033 Calcium hydroxide 74.10 K. 89.5 276-373 с Calcium oxide Carbon -4.52 x 1010 -4.891 x 100 -2.887 Cao 56.08 с K 41.84 2.03 273-1173 12.01 11.18 1.095 273-1373 с CO2 CO Carbon dioxide 44.01 1. 1. 1 36.11 4.233 7.464 0-1500 Carbon monoxide 28.01 28.95 0.4110 0.3548 -2.220 0-1500 Carbon tetrachloride CC4 Chlorine 153.84 70.91 63.54 93.39 12.98 273-343 Ch 1 °C 33.60 1.367 -1.607 6.473 0-1200 Соpper Cu 1. K 22.76 0.6117 273-1357
![TABLE B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol·K)] = a + bT + cT + dT Form 2: C,[kJ/(mol-C)] or [kJ/(mol-K)] = a + bT + cT? Example: (C,)acetone(e) = 0.07196 + (20.10 x 10-$)r - (12.78 x 10-8)7? + (34.76 x 10-12)Tr*, where T is in °C. %3D](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1590/0/5/6/4075ec655d7a186e1590056399297.jpg)








