Question: An object moving in a liquid experiences a linear drag force: F drag = (bv, direction opposite the motion), where b is a constant called
An object moving in a liquid experiences a linear drag force: F̅drag = (bv, direction opposite the motion), where b is a constant called the drag coefficient. For a sphere of radius R, the drag constant can be computed as b = 6πɳR, where ɳ is the viscosity of the liquid.
a. Use what you’ve learned in calculus to prove that
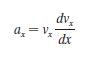
b. Find an algebraic expression for vx(x), the x-component of velocity as a function of distance traveled, for a spherical particle of radius R and mass m that is shot horizontally with initial speed v0 through a liquid of viscosity ɳ.
c. Water at 20ºC has viscosity ɳ = 1.0 × 10-3 N s/m2. Suppose a 1.0-cm-diameter, 1.0 g marble is shot horizontally into a tank of 20ºC water at 10 cm/s. How far will it travel before stopping?
Step by Step Solution
3.27 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a To prove that ax Vx dVxdx we can use Newtons second law F ma where Fdrag is the drag force m is th... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


