Question: Implement doubly linked lists by storing the sum of the next and prev pointers in a single pointer variable as described in Example 4.1. Example
Implement doubly linked lists by storing the sum of the next and prev pointers in a single pointer variable as described in Example 4.1.
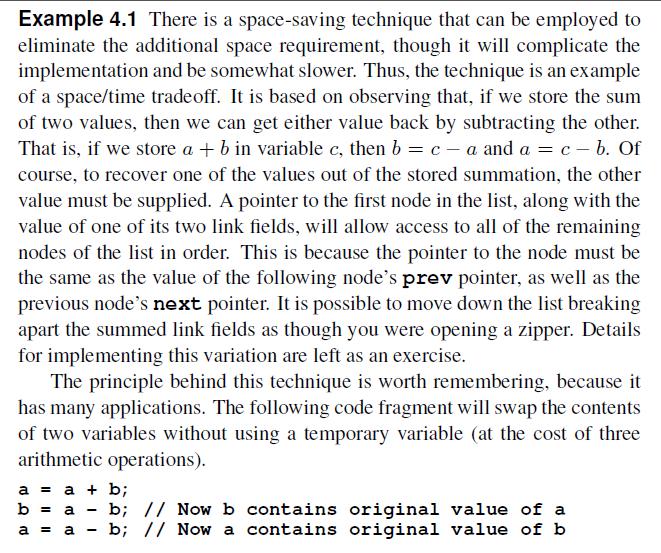
Example 4.1 There is a space-saving technique that can be employed to eliminate the additional space requirement, though it will complicate the implementation and be somewhat slower. Thus, the technique is an example of a space/time tradeoff. It is based on observing that, if we store the sum of two values, then we can get either value back by subtracting the other. That is, if we store a + b in variable c, then b = ca and a = c - b. Of course, to recover one of the values out of the stored summation, the other value must be supplied. A pointer to the first node in the list, along with the value of one of its two link fields, will allow access to all of the remaining nodes of the list in order. This is because the pointer to the node must be the same as the value of the following node's prev pointer, as well as the previous node's next pointer. It is possible to move down the list breaking apart the summed link fields as though you were opening a zipper. Details for implementing this variation are left as an exercise. The principle behind this technique is worth remembering, because it has many applications. The following code fragment will swap the contents of two variables without using a temporary variable (at the cost of three arithmetic operations). a = a + b; b = = a a = a - - b; // Now b contains original value of a b; // Now a contains original value of b
Step by Step Solution
3.30 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The technique described here is a classic example of a spacetime tradeoff Its based on the observati... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


