Brewster's Law If the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are complementary angles, the angle
Question:
Brewster's Law If the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are complementary angles, the angle of incidence is referred to as the Brewster angle θB. The Brewster angle is related to the index of refractions of the two media, n1 and n2, by the equation n1 sin θB = n2 cos θB, where n1 is the index of refraction of the incident medium and n2 is the index of refraction of the refractive medium. Determine the Brewster angle for a light beam traveling through water (at 20°C) that makes an angle of incidence with a smooth, flat slab of crown glass.
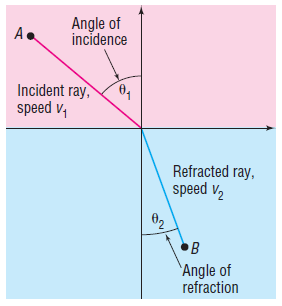
Light sound, and other waves travel at different speeds, depending on the media (air, water, wood, and so on) through which they pass. Suppose that light travels from a point A in one medium, where its speed is v1, to a point B in another medium, where its speed is v2. Refer to the figure, where the angle θ1 is called the angle of incidence and the angle θ2 is the angle of refraction. Snell's Law, which can be proved using calculus, states that 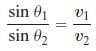
The vl/v2 is called the index of refraction. Some values are given in the table shown to the right.
Step by Step Answer:






