Question: Consider a microprocessor dissipating 50 W with dimensions 2-cm 2-cm square and 0.5-cm high (see figure). In order to cool the microprocessor, it is
Consider a microprocessor dissipating 50 W with dimensions 2-cm × 2-cm square and 0.5-cm high (see figure). In order to cool the microprocessor, it is necessary to mount it to a device called a heat sink, which serves two purposes. First, it distributes the heat from the relatively small microprocessor to a larger area; second, it provides extended heat transfer area in the form of fins. A small fan then is used to provide forced-air cooling. The main constraints to the design of a heat sink are cost and size. For laptop computers, fan power is also an important consideration. Develop a heat-sink design that maintains the microprocessor at 90°C or less and suggest ways to optimize the cooling system.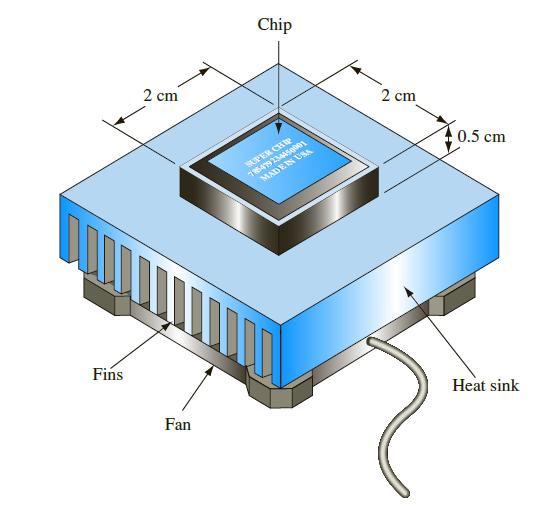
2 cm Fins Chip DOORBLY DOD Fan SUPER CHIP 715479 234450001 MADE IN USA 2 cm 0.5 cm Heat sink
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Solution The design is as follows i Heat sink HS base The HS base is made of copper with fins and a ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


