Light-emitting diodes or LEDs are currently perhaps the most energy-efficient lighting systems. Finned surface heat sinks are
Question:
Light-emitting diodes or LEDs are currently perhaps the most energy-efficient lighting systems. Finned surface heat sinks are used to cool high-intensity LED lighting that are used for spot and/or track lighting systems. A typical circular pin-fin heat sink is shown in the figure, and it is desirable that the fin-base temperature be less than 115°C to ensure efficient
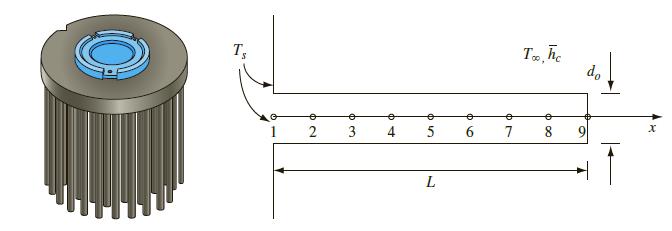
performance and longer life of the LED lamp. The fins are made of cold-forged, high-conductivity aluminum (k = 210 W/m K). Each pin has a diameter of 4 mm and a length of 40 mm. If the surrounding air is at 22°C, and it has a convection heat transfer coefficient of h̅c = 10 W/m2 K, determine the temperature distribution in the fin, considering convection from the fin tip and the heat transfer rate from the fin. Model it as a one-dimensional system, use a minimum of 9 nodes (including the ones at the base and tip) or more in your numerical scheme, and determine the effect of extra nodes. Compare the results with the one-dimensional fin analysis of Chapter 2. Also, if 90 such fins are evenly distributed on a 50-mm- diameter circular base, what is the maximum heat transfer rate that is dissipated by this heat sink so that the base temperature is less than 115°C? In a typical LED lamp, approximately 70% of the electric power (or wattage) is dissipated as heat (the remainder 30% is useful light). Determine the maximum power of the lamp, in watts, for which this heat sink is used.
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Heat Transfer
ISBN: 9781305387102
8th Edition
Authors: Frank Kreith, Raj M. Manglik, Mark S. Bohn





