Question
1. Strategy refers to the general policies that managers adopt to increase A. Costs. B. The number of client meetings. C. The rate of technological
1. Strategy refers to the general policies that managers adopt to increase
A. Costs.
B. The number of client meetings.
C. The rate of technological change.
D. The generation of profits.
2. As opposed to corporate strategy, business strategy is focused on
A. Increasing the elasticity of consumer demand.
B. The type of production technique to use.
C. The type of industry to produce in.
D. How to compete with other firms in the industry.
3. If transaction costs can be reduced in a marketplace, then total producer and consumer surplus will
A. Increase.
B. Stay the same.
C. Decrease.
D. Increase first and then decrease.
4. If consumers find that there are substantial transaction costs to purchasing a product, then
A. Overall consumer demand is greater at each price.
B. Overall consumer demand is the same at each price.
C. Overall consumer demand is less at each price.
D. Equilibrium price and quantity both fall.
5. In terms of business strategy, managers will attempt to adopt business strategies that
A. Maximize transaction costs.
B. Stabilize opportunity costs.
C. Minimize transaction costs.
D. Minimize sunk costs.
6. Dell Computer attempts to collect information about customers before purchase and assemble customized product for the customers. This process tries to
A. Reduce transaction costs for both Dell and the customer.
B. Reduce transaction costs for the customers only.
C. Increase transaction costs for Dell so that it can reduce taxable profits.
D. Increase transaction costs for customers so that IBM can also sell pcs.
7. The fast-food industry, from Back Yard Burgers to KFC, promises good food delivered quickly. The value of the consumer's time
A. Is less important than production costs.
B. Is a key component in creating value for the firm and the consumer.
C. Is usually so low that fast food is unimportant in the marketplace.
D. Must be discounted to make sure it is negative
8. Walmart, like many companies in the new economy, uses a hub-and-spoke distribution system to
A. Increase costs of stocking and inventory.
B. Change consumer attitudes toward warehouse shopping.
C. Decrease consumer demand.
D. Decrease costs of stocking and inventory.
9. Putting together two goods?shaving cream and razors?to increase value is using the power of
A. Complementary goods.
B. Substitute goods.
C. Unrelated goods.
D. Technologically advanced goods.
10. Which one of the following is a big problem in large groups?
A. Useless group leader
B. Adverse selection problem
C. Free-rider problem
D. Buyer-supplier conflicts
11. While CEO of General Electric, Jack Welch was a very successful corporate manager, he also loaded up his retirement program with numerous unusual benefits such as rented apartments, free airplanes, and numerous club memberships. The owners (stockholders) were generally unaware of these benefits. The source of conflict between owners and managers in this case was:
A. The choice of effort of Mr. Welch while he was CEO.
B. Perquisite taking on the part of Mr. Welch.
C. Differential risk exposure between Mr. Welch and the typical stockholder.
D. Overinvestment in company offices by Mr. Welch.
12. In most models of managerial conflict, the owner is the ______ and the manager is the
A. Wage earner; stockholder
B. Employee; director
C. Principal; agent
D. Resource; resource owner
13. Designing efficient contracts are costly when:
A. There is perquisite involved.
B. There is complete information.
C. There is asymmetric information.
D. There is an agency relationship.
14. Kaneshi Hartfield is a sales representative with Plain Truth Advertising. She is an excellent sales representative, but corporate management feels that she is too independent. But they are afraid to act, since Kaneshi maintains her own list of key contacts. This is an example of:
A. An asymmetric information problem.
B. Different time horizons of the sales representative and management.
C. The free rider problem.
D. The failure of bargaining.
15. Billy Mac Tailor drives an eighteen-wheeler CG Carriers. He always stops at All Bright truck stops to buy diesel fuel. He is a preferred customer and gets a free meal and shower worth $10.00. But All Bright charges $12.00 more for a fill up than most competitors. Which of the following is true?
A. CG Carriers gets a benefit of $22.00 because Tailor is a preferred customer.
B. CG Carriers has a wealth reduction of $2.00 even though they do not know about Tailor's actions.
C. There is a wealth transfer to Billy Mac Tailor and CG Carriers has a wealth reduction of $12.00.
D. Billy Mac Tailor increases his income by $10.00 and CG Carriers also benefits.
16. ______ makes designing efficient contracts costly.
A. Signaling
B. Self-selection
C. Huge monitoring costs for the principal
D. Huge monitoring costs for the agent
17. Which of the following statements is true?
A. Every game has a dominant strategy.
B. Not every game has a dominant strategy.
C. Every game has multiple Nash equilibria.
D. People never choose the strategies that result in Nash equilibrium.
18. Refer to Figure 9.5.
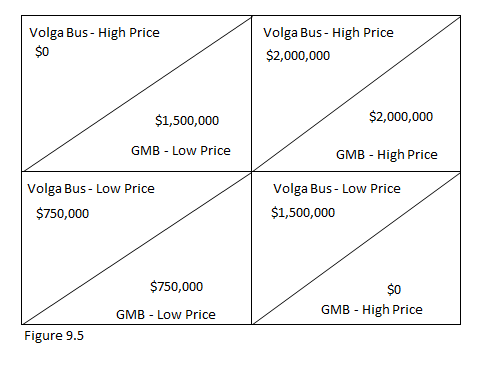
If the bus companies can expect to bid for contracts every 6?12 months for new buses, then the outcome may shift to
A. GMB?High, volgabus?High.
B. GMB?Low, volgabus?High.
C. GMB?High, volgabus?Low.
D. GMB?Low, volgabus?Low.
19. Identify the statement that best defines Nash equilibrium.
A. It is a set of strategies in which a firm does the best it can, given the action of its rival.
B. It is a sequence of actions, where the actions are taken at each node of the game.
C. It is a set of strategies that gives a player the first-mover advantage.
D. It is a sequence of actions that are taken to influence the actions of rivals.
20. Which of the following can be used to predict the outcome of a game if there are no dominant strategies in the game?
A. Secure strategy
B. Nash equilibrium
C. First-mover advantage
D. Prisoner?s dilemma
21. When there are large network effects of adopting a new technology, firms often feel that government regulation or joint ventures can solve the
A. Problem of excessive investment.
B. Coordination problem.
C. Problem of excess capacity.
D. Market inefficiency problem.
22. The benefit of a mixed strategy is
A. Higher returns for both the players in the market.
B. Lower risks for both the players in the market.
C. The element of consistency that baffles rivals.
D. The element of surprise that baffles rivals.
23. In the Battle of the Sexes game, Man likes to go to watch football, while Woman likes to go to the mall. Both of them would rather go together than go alone. They decide to show up to one of these places without contacting each other. A game like this will have
A. A dominant strategy for Man and none for Women.
B. One dominant strategy for both the players.
C. No Nash equilibrium strategies.
D. A Nash equilibrium in mixed strategies
24. Which of the following is a difference between a pure strategy and a mixed strategy?
A. When a player chooses a specific action in a game, it is a pure strategy, while in a mixed strategy players randomize.
B. When a player assigns a probability to an action, it is a pure strategy, while in a mixed strategy players choose their actions sequentially.
C. A pure strategy has an element of surprise, while a mixed strategy can be easily predicted by rivals.
D. A pure strategy involves all players making their moves simultaneously, while a mixed strategy minimizes the losses of players.
25. Actions like entering a new market, pricing a new product, or making a bid to buy another company are all useful Nash-like managerial decisions because they are
A. Repeated often and the outcome depends on the coordination of decisions with rivals.
B. Not repeated often and the outcome depends on the coordination of decisions with rivals.
C. Repeated often and the outcome depends on the simultaneous decisions of rivals.
D. Not repeated often and the outcome depends on the simultaneous decisions of rivals.
Volga Bus- High Price $0 $1,500,000 GMB - Low Price Volga Bus-Low Price $750,000 Figure 9.5 $750,000 GMB - Low Price Volga Bus- High Price $2,000,000 $2,000,000 GMB - High Price Volga Bus-Low Price $1,500,000 $0 GMB - High Price
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 D the generation of profits 2 D how to compete with other firms in the industry 3 A increase 4 C o...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


