Question
Compute P(S|F), P(N|F), P(S|U), P(N|U) as well as P(F) and P(U) A major use of decision tree analysis is to estimate the expected value of
Compute P(S|F), P(N|F), P(S|U), P(N|U) as well as P(F) and P(U)
A major use of decision tree analysis is to estimate the expected value of information. We will use the following simple example to illustrate the application process.
In this case, a CEO needs to decide whether to invest $5 million to improve an existing product, which is sure to yield a profit of $7 million, or to develop a new product, which will yield a profit of $15 million if successful or $0 if not successful. A consultant offers to conduct a market forecast for the new product for a fee of $0.5 million. Should the CEO hire the consultant and in which product should the CEO invest?
A 2-stage tree shown below describes the decision process: the first stage is to decide whether to acquire the information; the second stage is to decide which product to invest. For simplicity, we assume that the CEO is risk-neutral and wants to maximize the expected net profit.
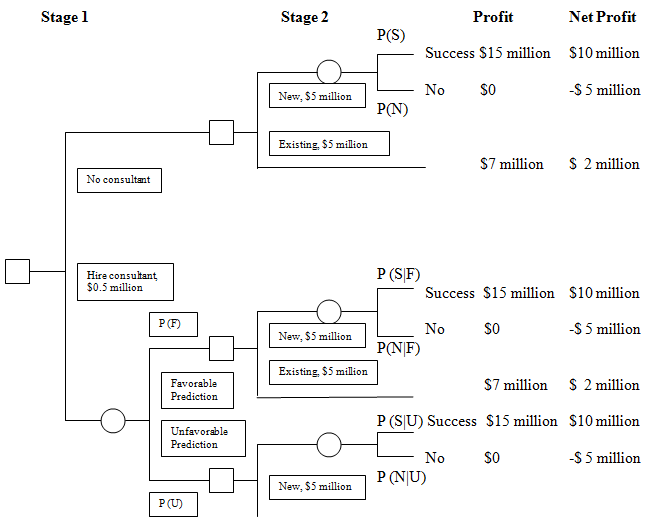
Stage 1 No consultant Hire consultant, $0.5 million P (F) Favorable Prediction Unfavorable Prediction P(U) Stage 2 New, $5 million Existing, $5 million New, $5 million Existing, $5 million New, $5 million P(S) P(N) P (SF) P(NF) Profit Success $15 million $10 million No No SO No $7 million P (NU) Success $15 million $10 million SO P (SU) Success $15 million SO Net Profit $7 million -$ 5 million $ 2 million -$ 5 million $ 2 million $10 million -$5 million
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
PSF05X15 5 25 PNF...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


