Consider the daily market for hot dogs in a small city. Suppose that this market is in long-run competitive equilibrium with many hot dog stands
Consider the daily market for hot dogs in a small city. Suppose that this market is in long-run competitive equilibrium with many hot dog stands in the city, each one selling the same kind of hot dogs. Therefore, each vendor is a price taker and possesses no market power.
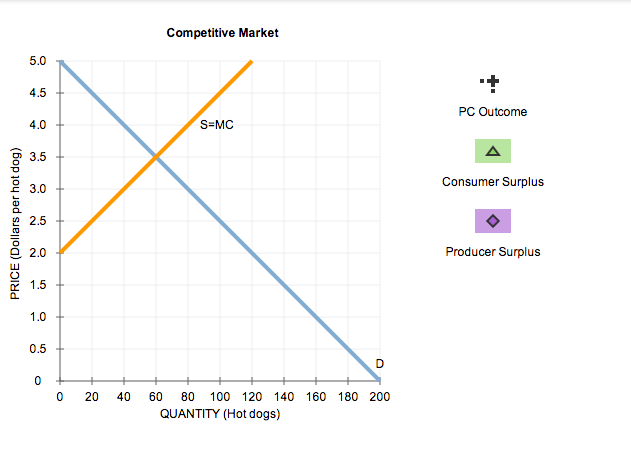
The following graph shows the demand (D) and supply curves (S = MC) in the market for hot dogs.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the market price and quantity that will result from competition. Use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area that represents consumer surplus, and use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area that represents producer surplus.
Assume that one of the hot dog vendors successfully lobbies the city council to obtain the exclusive right to sell hot dogs within the city limits. This firm buys up all the rest of the hot dog vendors in the city and operates as a monopoly. Assume that this change doesn't affect demand and that the new monopoly's marginal cost curve corresponds exactly to the supply curve on the previous graph. Under this assumption, the following graph shows the demand (D), marginal revenue (MR), and marginal cost (MC) curves for the monopoly firm.
Place the black point (plus symbol) on the following graph to indicate the profit-maximizing price and quantity of a monopolist. Use the green points (triangle symbol) to shade the area that represents consumer surplus, and use the purple points (diamond symbol) to shade the area that represents producer surplus.
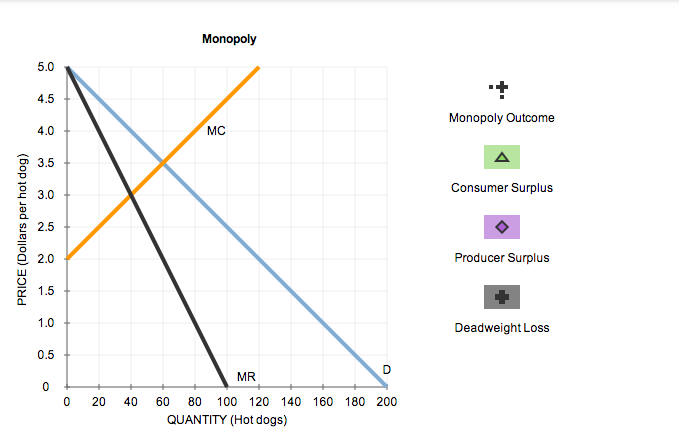
Consider the welfare effects when the industry operates under a competitive market versus a monopoly.
On the monopoly graph, use the black points (plus symbol) to shade the area that represents the loss of welfare from a monopoly, or dead weight loss. That is, show the area that was formerly producer surplus or consumer surplus and now does not accrue to anybody.
Dead weight loss occurs when a monopoly controls a market because the resulting equilibrium is different from the competitive outcome, which is efficient.
In the following table, enter the price and quantity that would arise in a competitive market; then enter the profit-maximizing price and quantity that would be chosen if a monopolist controlled this market. 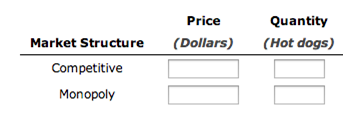 Given the summary table of the two different market structures, you can infer that, in general, the price is higher under a monopoly, competitive market and the quantity is lower under a_______________.
Given the summary table of the two different market structures, you can infer that, in general, the price is higher under a monopoly, competitive market and the quantity is lower under a_______________.
PRICE (Dollars per hot dog) 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 0 20 Competitive Market S=MC D + + 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 QUANTITY (Hot dogs) + PC Outcome A Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus PRICE (Dollars per hot dog) 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 0 20 40 Monopoly MC MR D 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 QUANTITY (Hot dogs) Monopoly Outcome A Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Deadweight Loss Market Structure Competitive Monopoly Price (Dollars) Quantity (Hot dogs)
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Following are the required diagram This is the case of perfect competition green colored are...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


