Question
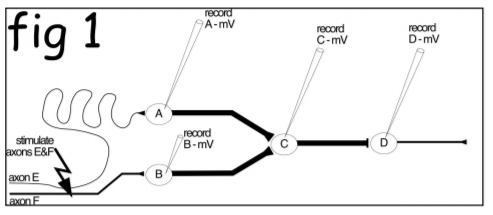
Figure 1 shows a fictitious neural circuit, which includes parts of 6 neurons: A, B,C,D and the axons of cells E and F. A-D are
Figure 1 shows a fictitious neural circuit, which includes parts of 6 neurons: A, B,C,D and the axons of cells E and F. A-D are simple cells with a soma and axon but no dendrites. Cell A makes nicotinic, cholinergic excitatory synaptic connection onto Cell C; cell B makes a glutamatergic (AMPA receptor) synapse onto cell C, which in turn makes an inhibitory synaptic connection, via GABA acting on GABAA receptors with Cell D. Cell D uses ATP as its fast transmitter. Recording microelectrodes in the cell bodies of A,B,C&D measure the membrane potential (Vm) of each cell, over 190ms. We We do not record cells E and F, but we can stimulate their axons together (at the jagged arrow) with a stimulating electrode. Note that axons of A,B and C are thick; axons of D&F are of intermediate diameter and axon of cell E is very thin. Cell F uses 5-HT (acting on 5-HT3 receptors) as its transmitter and cells D and E are both purinergic, releasing ATP onto P2x receptors.
? Figure 2 shows Vm of neurons A-D, in millivolts over a period of about 190ms. ? All four cells are initially at their resting membrane potentials (shown by black dashed lines). ? We apply a small shock, via a stimulating electrode (a small stimulus artefact appears simultaneously on all 4 traces), which initiates 1 action potential in axon E and 1 in axon F at exactly the same moment. ? Action potentials in E&F then travel down to their terminals and evoke excitatory post-synaptic potentials in both cell A and cell B, triggering one action potential in A and two in B. ? Action potentials in A and B then propagate down their respective axons, leading to summating excitatory synaptic potentials in Cell C, which also fires an action potential ? Cell C's action potential then propagates down its axon, eventually releasing gamma amino butyric acid which acts on GABAA receptors on cell D, causing an inhibitory synaptic potential.
In Figure2 overleaf, 20 features of the recordings are marked in blue. Below it is a list describing 26 neural characteristics (A-Z). Match each feature (1-20) with the characteristic (A-Z) that best describes it (obviously not all the characteristics correspond to a feature). In cases where 2 answers may be correct - choose the most comprehensive one. Write your answers on the answer sheet at the back of the printout. No answer is used more than once. Single ended arrows point to a moment or a feature; double ended arrows show a duration or amplitude or difference. 9 and 14 show delay between the closest points on the dashed lines/
fig 1 viva stimulate axons E&F axon E Laxon E B record A-mV record B-mV 0 record C-mV record D-mV
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
LIST OF CHARACTERISTICS AZ A overshoot of an action potential B threshold of an action potential C moment where chloride current is operating D firing ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


